smart card authentication example Roland Moreno patented the memory card in 1974. By 1977, three commercial manufacturers, Bull CP8, SGS Thomson, and Schlumberger, started developing smart card products. In March 1979, Michel Hugon from Bull CP8 was the first to design and . See more Auburn's Chris Davis returns Alabama's missed field goal for a 109-yard field goal to beat Alabama in the 2013 Iron Bowl.
0 · smart card multi factor authentication
1 · smart card identity
2 · smart card based identification system
3 · smart card authentication step by
4 · smart card authentication protocol
5 · enable smart card log on
6 · enable smart card authentication
7 · authenticate using your smart card
Open source NFC Reader & Writer. Read and write NFC tags online, and offline. - codemysoul/webnfc. . It is built using very basic HTML, CSS and JavaScript. With service .
It integrates a microprocessor, some memory, and some apps. The circular metal contact is vital to connect to the chip below and activate the card electrically. It's used with a contact or contactless card reader(POS for payments, at the ATM, or even on your mobile phone). Why? The card reader (or mobile phone) . See moreIn the form of credit cards and SIM cards, smart cardsare the most common form of IT processing power on the planet. It is estimated that . See moreAccording to Markets and Markets' recent research report, the smart card marketvalueis expected to reach .9 billion by 2026. . See moreAccording to the 11 February 2023Eurosmartforecasts, smart card markets will probably exceed 10 billion units in 2022. The . See more
Roland Moreno patented the memory card in 1974. By 1977, three commercial manufacturers, Bull CP8, SGS Thomson, and Schlumberger, started developing smart card products. In March 1979, Michel Hugon from Bull CP8 was the first to design and . See moreSmart Card Authentication is a means of verifying users into enterprise resources such as workstations and applications using a physical card in tandem with a smart card reader and .
As a National eID card, smart health card, residence permit, or electronic passport, smart card technology offers more robust identification and authentication tools for both authorities' and citizens' benefits.
Smart Card Authentication is a means of verifying users into enterprise resources such as workstations and applications using a physical card in tandem with a smart card reader and software on the workstation. Learn how 1Kosmos enhances smart card authentication with BlockID, offering biometric-based security, identity proofing, privacy by design, distributed ledger technology, interoperability, and industry certifications. Storing the cryptographic keys in a secure central location makes the authentication process scalable and maintainable. For smart cards, Windows supports a provider architecture that meets the secure authentication requirements and is extensible so that you can include custom credential providers. The process: The user puts the smart card into a card reader hooked up to the device or system they want to use. The card reader talks to the smart card, asking the user to enter a password or give fingerprints to prove who they are.
This section describes what a smart card is and how smart card authentication works. It describes the tools that you can use to read and manipulate smart card content. It also provides sample use cases and describes the setup of both the IdM server and IdM client for smart card authentication. Smart card authentication is a two-step login process that uses a smart card. The smart card stores a user’s public key credentials and a personal identification number (PIN), which acts as the secret key to authenticate the user to the smart card. Funny enough, the example translates to how secure email is implemented using public key cryptography. How public key authentication works. In its most simple form, public key authentication as follows: The server sends Alice a random string (nonce). Smart card authentication is a method that employs the embedded chip in the card to verify the identity of the user certificates. The chip can generate or store authentication data through cryptographic algorithms that a reader can verify.
Certificate-based authentication is an encrypted method that enables devices and people to identify themselves to other devices and systems. Two common examples are a smart card or when an employee’s device sends a digital certificate to a network or server.
As a National eID card, smart health card, residence permit, or electronic passport, smart card technology offers more robust identification and authentication tools for both authorities' and citizens' benefits.Smart Card Authentication is a means of verifying users into enterprise resources such as workstations and applications using a physical card in tandem with a smart card reader and software on the workstation. Learn how 1Kosmos enhances smart card authentication with BlockID, offering biometric-based security, identity proofing, privacy by design, distributed ledger technology, interoperability, and industry certifications. Storing the cryptographic keys in a secure central location makes the authentication process scalable and maintainable. For smart cards, Windows supports a provider architecture that meets the secure authentication requirements and is extensible so that you can include custom credential providers.
The process: The user puts the smart card into a card reader hooked up to the device or system they want to use. The card reader talks to the smart card, asking the user to enter a password or give fingerprints to prove who they are.This section describes what a smart card is and how smart card authentication works. It describes the tools that you can use to read and manipulate smart card content. It also provides sample use cases and describes the setup of both the IdM server and IdM client for smart card authentication. Smart card authentication is a two-step login process that uses a smart card. The smart card stores a user’s public key credentials and a personal identification number (PIN), which acts as the secret key to authenticate the user to the smart card. Funny enough, the example translates to how secure email is implemented using public key cryptography. How public key authentication works. In its most simple form, public key authentication as follows: The server sends Alice a random string (nonce).
Smart card authentication is a method that employs the embedded chip in the card to verify the identity of the user certificates. The chip can generate or store authentication data through cryptographic algorithms that a reader can verify.
shell club smart card catalog
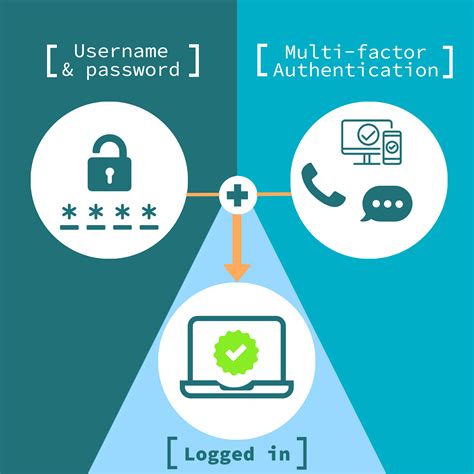
smart card multi factor authentication
smart card identity

1. Bring the phone near an NFC terminal. The phone recognizes to bring up Apple Pay. 2. Double-press side button. Face ID passes and the phone says "Hold near reader". 3. Nothing. It doesn't further communicate with the terminal. Or 1. Double-click the side button. Face ID passes and the phone says "Hold near reader". 2. Bring the phone near .
smart card authentication example|enable smart card authentication