rfid tag failure modes Abstract—In this work the failure modes and mechanisms are investigated of a commercially available RFID tag, when it is exposed to extreme temperatures well beyond specifications. Both erroneous functioning and malfunctioning are observed after a thermal cycle exposing the tag to an elevated temperature in the 300-550 C range.
Press [Screen Device Settings]. Press [External Interface Software Settings]. .
0 · Reliability and failure analysis of UHF RFID passive tags
1 · RFID 401
2 · Mastering RFID Label Converting
item 8 26/40PCS Amiibo NFC Zelda Tears of the Kingdom Breath of The Wild Square Card .
Studies show that 1%-5% of RFID labels fail during the converting phase with electrostatic discharge being a key cause. Specifications for the sensitivity of electronic devices, including RFID chips, are based on well-researched and proven test methods developed by the .
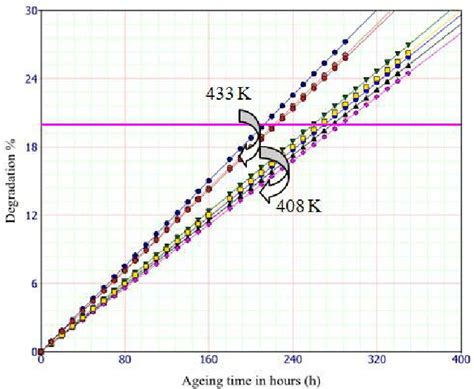
It is observed that the failure mechanisms depend on the type of passive tags and the values of .Studies show that 1%-5% of RFID labels fail during the converting phase with electrostatic discharge being a key cause. Specifications for the sensitivity of electronic devices, including RFID chips, are based on well-researched and proven test .It is observed that the failure mechanisms depend on the type of passive tags and the values of selected storage temperatures for the tests. The scale parameters of M1 tags aged at 413 K are around 280 hours, whereas the scale parameters of the M2 tags aged at same temperature are around 360 hours.
In this work the failure modes and mechanisms are investigated of a commercially available RFID tag, when it is exposed to extreme temperatures well beyond specifications. Both erroneous functioning and malfunctioning are observed after a thermal cycle exposing the tag to an elevated temperature in the 300-550 °C range.
Abstract—In this work the failure modes and mechanisms are investigated of a commercially available RFID tag, when it is exposed to extreme temperatures well beyond specifications. Both erroneous functioning and malfunctioning are observed after a thermal cycle exposing the tag to an elevated temperature in the 300-550 C range.Failure mode and failure site can be identified through data analysis gained from performance evaluation, nondestructive analysis and destructive physical analysis technology, based on which failure mechanism,Common Failure Modes Consideration of product failure modes is necessary in any discussion of tag reliability, tag durability and the differences among tags. RFID tags fail in several ways. For example: • High electrical resistance can develop between the chip and the antenna. Possible causes include corrosion or oxidation in the
As an introduction to RFID tags on-line testing, a Failure Modes and Effects Analysis first describes the effects of the potential defects on these systems. Second, a SystemC model of the RFID system is proposed as a way to evaluate the proposed test solutions.Sporadically, the RFID tag returns a wrong identification code after extreme thermal cycling. This effect is caused by relatively weak bits flipping from '1' to '0' and seems consistent with existing retention models.
Sporadically, the RFID tag returns a wrong identification code after extreme thermal cycling. This effect is caused by relatively weak bits flipping from “1” to “0” and seems consistent with existing retention models.
In order to pass qualification tests, a passive RFID tags needs to respond to queries by a tag reader. There was an unacceptable level of failures of passive RFID tags after exposure to cyclic testing (-40 to 70°C, 95 %RH) and damp heat storage (85°C, 85 %RH) tests.Studies show that 1%-5% of RFID labels fail during the converting phase with electrostatic discharge being a key cause. Specifications for the sensitivity of electronic devices, including RFID chips, are based on well-researched and proven test .It is observed that the failure mechanisms depend on the type of passive tags and the values of selected storage temperatures for the tests. The scale parameters of M1 tags aged at 413 K are around 280 hours, whereas the scale parameters of the M2 tags aged at same temperature are around 360 hours.In this work the failure modes and mechanisms are investigated of a commercially available RFID tag, when it is exposed to extreme temperatures well beyond specifications. Both erroneous functioning and malfunctioning are observed after a thermal cycle exposing the tag to an elevated temperature in the 300-550 °C range.
Abstract—In this work the failure modes and mechanisms are investigated of a commercially available RFID tag, when it is exposed to extreme temperatures well beyond specifications. Both erroneous functioning and malfunctioning are observed after a thermal cycle exposing the tag to an elevated temperature in the 300-550 C range.
Reliability and failure analysis of UHF RFID passive tags
Failure mode and failure site can be identified through data analysis gained from performance evaluation, nondestructive analysis and destructive physical analysis technology, based on which failure mechanism,
Common Failure Modes Consideration of product failure modes is necessary in any discussion of tag reliability, tag durability and the differences among tags. RFID tags fail in several ways. For example: • High electrical resistance can develop between the chip and the antenna. Possible causes include corrosion or oxidation in the As an introduction to RFID tags on-line testing, a Failure Modes and Effects Analysis first describes the effects of the potential defects on these systems. Second, a SystemC model of the RFID system is proposed as a way to evaluate the proposed test solutions.Sporadically, the RFID tag returns a wrong identification code after extreme thermal cycling. This effect is caused by relatively weak bits flipping from '1' to '0' and seems consistent with existing retention models.
Sporadically, the RFID tag returns a wrong identification code after extreme thermal cycling. This effect is caused by relatively weak bits flipping from “1” to “0” and seems consistent with existing retention models.
RFID 401
Unburdening WeWork members from having to carry (sometimes multiple) physical cards to gain access to spaces and amenities gave reason to start looking into creating door-hardware agnostic solutions. Starting with a simple .
rfid tag failure modes|Reliability and failure analysis of UHF RFID passive tags