how many frequencies can a rfid chip do at once Advantages of High-Frequency (HF) Chips. The NXP ICODE® chip series operates at a frequency of 13.56 MHz, which falls within the high-frequency (HF) RFID range. Compared to . The way amiibos work is that some sections of the tag, (those that determine what amiibo it is) .
0 · what does rfid work over
1 · rfid frequency range
2 · rfid band frequency
3 · radio frequency rfid
4 · low frequency rfid range
5 · low frequency rfid
6 · how much rfid holds
7 · how long does rfid work
In this mode, Hunter Cat NFC emulates a NFC tag. It doesn’t initiate the communication, it only responds to a NFC reader. A typical application of the card emulation mode is how people use NFC in their smartphones to replace .Information. NFC Tools GUI is a cross Platform software : it works on Mac, Windows and Linux. You can read and write your NFC chips with a simple and lightweight user interface. Connect your NFC reader to your computer like the very popular ACR122U to start playing with your NFC .
Generally speaking, RFID systems are mainly divided into the following three types: LF RFID, HF RFID, and UHF RFID. The operating frequency of LF RFID is 125kHz-134.2 kHz. The operating frequency of HF RFID is 13.56MHz. The amount of data that can be stored in an RFID tag depends on factors such as the type of tag, the memory capacity of the tag, and the specific application requirements. .
High Frequency RFID is very common, and operates in a frequency range from 3 to 30 MHz. The read distance ranges from 10 centimeters to 1 meter. The majority of HF RFID .Advantages of High-Frequency (HF) Chips. The NXP ICODE® chip series operates at a frequency of 13.56 MHz, which falls within the high-frequency (HF) RFID range. Compared to . Which Frequencies Does RFID Use? To enable noncontact data exchange via an RFID system, radio waves are used for communication. Depending on the application . By analyzing the RFID chip datasheet, you can gather vital information about the supported frequency range of the RFID chip, assisting you in accurately determining the RFID .
what does rfid work over
This article will analyze in detail the characteristics and application differences of the three RFID frequencies: LF (low frequency), HF (high frequency), and UHF (ultra-high frequency).This article provides a guide on RFID Frequency Ranges: LF, HF, UHF, and Microwave. We will explore how these frequencies enable a variety of applications, providing clarity to make .Learn how to choose the right RFID frequency for your system with this step-by-step guide. Explore the differences between LF, HF, and UHF, and optimize performance and cost for .
Generally speaking, RFID systems are mainly divided into the following three types: LF RFID, HF RFID, and UHF RFID. The operating frequency of LF RFID is 125kHz-134.2 kHz. The operating frequency of HF RFID is 13.56MHz. The amount of data that can be stored in an RFID tag depends on factors such as the type of tag, the memory capacity of the tag, and the specific application requirements. RFID tags can be categorized into two main types based . High Frequency RFID is very common, and operates in a frequency range from 3 to 30 MHz. The read distance ranges from 10 centimeters to 1 meter. The majority of HF RFID devices function at 13.56 MHz, with moderate radio interference sensitivity.The characteristics of each band affect the RFID range differently. Here’s how. In general, the higher the frequency, the greater is the range. RF radiation has more energy at the higher frequencies and so the RF field can influence RFID tags that are further away.
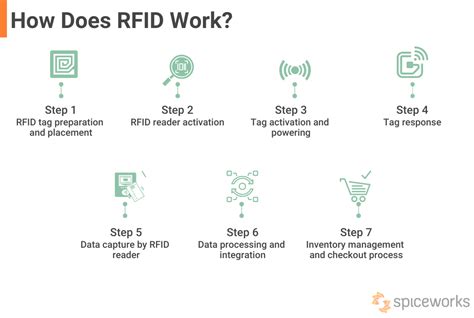
Advantages of High-Frequency (HF) Chips. The NXP ICODE® chip series operates at a frequency of 13.56 MHz, which falls within the high-frequency (HF) RFID range. Compared to ultra-high frequency (UHF) RFID, high-frequency RFID offers the following advantages: Shorter Reading Distance: Typically between 1 and 2 meters, making it more effective . Which Frequencies Does RFID Use? To enable noncontact data exchange via an RFID system, radio waves are used for communication. Depending on the application requirements, RFID systems utilize different frequency ranges. By analyzing the RFID chip datasheet, you can gather vital information about the supported frequency range of the RFID chip, assisting you in accurately determining the RFID frequency for your system.
This article will analyze in detail the characteristics and application differences of the three RFID frequencies: LF (low frequency), HF (high frequency), and UHF (ultra-high frequency).This article provides a guide on RFID Frequency Ranges: LF, HF, UHF, and Microwave. We will explore how these frequencies enable a variety of applications, providing clarity to make informed decisions in the exciting world of radio frequency identification.
Learn how to choose the right RFID frequency for your system with this step-by-step guide. Explore the differences between LF, HF, and UHF, and optimize performance and cost for your RFID applications.
Generally speaking, RFID systems are mainly divided into the following three types: LF RFID, HF RFID, and UHF RFID. The operating frequency of LF RFID is 125kHz-134.2 kHz. The operating frequency of HF RFID is 13.56MHz. The amount of data that can be stored in an RFID tag depends on factors such as the type of tag, the memory capacity of the tag, and the specific application requirements. RFID tags can be categorized into two main types based . High Frequency RFID is very common, and operates in a frequency range from 3 to 30 MHz. The read distance ranges from 10 centimeters to 1 meter. The majority of HF RFID devices function at 13.56 MHz, with moderate radio interference sensitivity.
The characteristics of each band affect the RFID range differently. Here’s how. In general, the higher the frequency, the greater is the range. RF radiation has more energy at the higher frequencies and so the RF field can influence RFID tags that are further away.Advantages of High-Frequency (HF) Chips. The NXP ICODE® chip series operates at a frequency of 13.56 MHz, which falls within the high-frequency (HF) RFID range. Compared to ultra-high frequency (UHF) RFID, high-frequency RFID offers the following advantages: Shorter Reading Distance: Typically between 1 and 2 meters, making it more effective . Which Frequencies Does RFID Use? To enable noncontact data exchange via an RFID system, radio waves are used for communication. Depending on the application requirements, RFID systems utilize different frequency ranges. By analyzing the RFID chip datasheet, you can gather vital information about the supported frequency range of the RFID chip, assisting you in accurately determining the RFID frequency for your system.
This article will analyze in detail the characteristics and application differences of the three RFID frequencies: LF (low frequency), HF (high frequency), and UHF (ultra-high frequency).This article provides a guide on RFID Frequency Ranges: LF, HF, UHF, and Microwave. We will explore how these frequencies enable a variety of applications, providing clarity to make informed decisions in the exciting world of radio frequency identification.
rfid frequency range
rfid band frequency
radio frequency rfid
super smart cards
Some tags can be read and written, while others are read-only or encrypted. Only the NFC Data Exchange Format (NDEF) is discussed in this tutorial. Adding NFC Support in .
how many frequencies can a rfid chip do at once|rfid frequency range