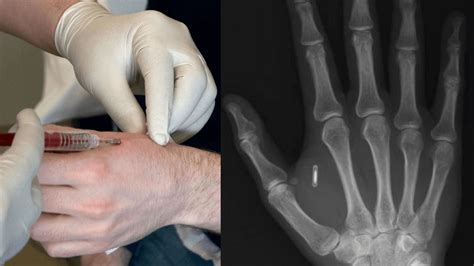
microchip rfid chip A human microchip implant is any electronic device implanted subcutaneously (subdermally) usually via an injection. Examples include an identifying integrated circuit RFID device encased in silicate glass which is implanted in the body of a human being. 3. Swipe down from the top-right corner of the screen (on iPhone X) or swipe up from the bottom of the screen (on older iPhones) to access the Control Center and tap the NFC Tag Reader option. After that, try scanning a .
0 · where are rfid chips used
1 · what is an rf chip
2 · what are rfid chips
3 · rfid microchip for pets
4 · rfid in humans
5 · microchip rfid devices
6 · how to disable rfid implant
7 · how to disable microchip implants
Languages. Kotlin 100.0%. Android NFC read and write example. Contribute to codexpedia/android_nfc_read_write development by creating an account on GitHub.
Our RFID chips are suitable for the smallest devices and don’t require any external components, which reduces the cost of your tag. These identification ICs are available as die-on-wafers with optional gold bumps, packaged die or an . Other payment implants are based on radio-frequency identification (RFID), which is the similar technology typically found in physical .
Our RFID chips are suitable for the smallest devices and don’t require any external components, which reduces the cost of your tag. These identification ICs are available as die-on-wafers with optional gold bumps, packaged die or an entire transponder. Other payment implants are based on radio-frequency identification (RFID), which is the similar technology typically found in physical contactless debit and credit cards.
A human microchip implant is any electronic device implanted subcutaneously (subdermally) usually via an injection. Examples include an identifying integrated circuit RFID device encased in silicate glass which is implanted in the body of a human being. RFID microchips, embedded under the skin with a procedure that’s already cheap and available, provide a digital interface to the real world centered about the holder’s identity: your ID, credit card information, bus pass, library card, and many other sources of information you currently carry in your purse/wallet can instead be stored on an . Sure, the technology—a millimeters-long microchip equipped with near-field communication capabilities and lodged just under the skin—had a niche, cutting-edge appeal, but in practical. Chips sold for implants are generally either low or high frequency. RFID chips are identified using radio waves, and near-field communication (NFC) chips are a branch of high-frequency.
An RFID (Radio Frequency Identification) chip is a small device that uses radio waves to transmit data wirelessly. It consists of a microchip and an antenna, encapsulated in a tiny package. These chips are often embedded in various items, such as cards, tags, labels, or even implanted in living beings.
The ATA5577C is a contactless read/write Identification Integrated Chip (IDIC®) for applications in the 125 kHz or 134 kHz frequency band. A single coil connected to the chip serves as the IC’s power supply and bidirectional
Three Square Market CEO Todd Westby enters the company's office by holding his microchipped hand near an RFID reader. A year into their experiment, McMullan and a few employees say they are.Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) systems use radio frequency to identify, locate and track people, assets and animals. Passive RFID systems are composed of three components – a reader (interroga-tor), passive tag and host computer. The tag is com-posed of an antenna coil and a silicon chip that includes basic modulation circuitry and non .Our RFID chips are suitable for the smallest devices and don’t require any external components, which reduces the cost of your tag. These identification ICs are available as die-on-wafers with optional gold bumps, packaged die or an entire transponder. Other payment implants are based on radio-frequency identification (RFID), which is the similar technology typically found in physical contactless debit and credit cards.
A human microchip implant is any electronic device implanted subcutaneously (subdermally) usually via an injection. Examples include an identifying integrated circuit RFID device encased in silicate glass which is implanted in the body of a human being. RFID microchips, embedded under the skin with a procedure that’s already cheap and available, provide a digital interface to the real world centered about the holder’s identity: your ID, credit card information, bus pass, library card, and many other sources of information you currently carry in your purse/wallet can instead be stored on an . Sure, the technology—a millimeters-long microchip equipped with near-field communication capabilities and lodged just under the skin—had a niche, cutting-edge appeal, but in practical. Chips sold for implants are generally either low or high frequency. RFID chips are identified using radio waves, and near-field communication (NFC) chips are a branch of high-frequency.
An RFID (Radio Frequency Identification) chip is a small device that uses radio waves to transmit data wirelessly. It consists of a microchip and an antenna, encapsulated in a tiny package. These chips are often embedded in various items, such as cards, tags, labels, or even implanted in living beings.The ATA5577C is a contactless read/write Identification Integrated Chip (IDIC®) for applications in the 125 kHz or 134 kHz frequency band. A single coil connected to the chip serves as the IC’s power supply and bidirectional Three Square Market CEO Todd Westby enters the company's office by holding his microchipped hand near an RFID reader. A year into their experiment, McMullan and a few employees say they are.

where are rfid chips used
what is an rf chip

what are rfid chips
rfid microchip for pets
rfid in humans
About Us. WEGL Radio is Auburn University’s student-operated, student-funded radio station, and it is unlike any other organization that you will encounter on Auburn’s campus. WEGL was not the first radio station at Auburn University. .
microchip rfid chip|what are rfid chips