sw1 sw2 smart card • Protocol data unit See more Saturday, January 4, 1997NFC: Green Bay Packers 35, San Francisco 49ers 14The Packers defense forced five turnovers en route to victory, while See more
0 · What are APDUs
1 · Smart card application protocol data unit
2 · ISO7816 Standard Overview
3 · APDU (Application Protocol Data Unit)
Please sign up to create a new account to manage your proofs and order status, .
What are APDUs
smart card types
Smart card application protocol data unit
A command APDU is sent by the reader to the card – it contains a mandatory 4-byte header (CLA, INS, P1, P2) [2] and from 0 to 65 535 bytes of data. A response APDU is sent by the card to the reader – it contains from 0 to 65 536 bytes of data, and 2 mandatory status bytes (SW1, SW2). See moreIn the context of smart cards, an application protocol data unit (APDU) is the communication unit between a smart card reader and a smart card. The structure of the APDU is defined by ISO/IEC 7816-4 . See more• Protocol data unit See more
• Smartcard ISOs, contents• Selected list of smartcard APDU commands• Selected list of SW1 SW2 Status bytes• More information about APDU commands and APDU responses See moreIn the context of smart cards, an Application Protocol Data Unit (APDU) is the unit of communication between a smart card reader and a smart card. The structure of the APDU is .When SW1 is neither E nor D, the card support the instruction. This part of ISO7816 does not interprets neither X SW1 bytes, nor SW2 bytes; Their meaning relates to the application .
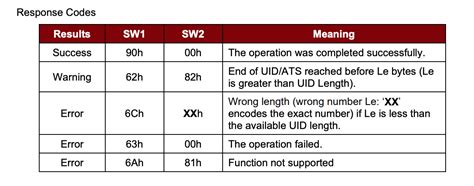
Status Word (SW1, SW2): Consists of two bytes that provide information about the status of the operation (e.g., success, error, warnings). The status word codes are typically .A command APDU is sent by the reader to the card – it contains a mandatory 4-byte header (CLA, INS, P1, P2) [2] and from 0 to 65 535 bytes of data. A response APDU is sent by the card to the reader – it contains from 0 to 65 536 bytes of data, and 2 mandatory status bytes (SW1, SW2).
smart card service
In the context of smart cards, an Application Protocol Data Unit (APDU) is the unit of communication between a smart card reader and a smart card. The structure of the APDU is defined by ISO/IEC 7816-4, which specifies organization, security, and commands for .When SW1 is neither E nor D, the card support the instruction. This part of ISO7816 does not interprets neither X SW1 bytes, nor SW2 bytes; Their meaning relates to the application itself. The end sequence SW1-SW2 gives the card status at the end of the command. Status Word (SW1, SW2): Consists of two bytes that provide information about the status of the operation (e.g., success, error, warnings). The status word codes are typically provided by the hardware manufacturer. Tables 13 to 18 specify values of SW2 when SW1 is valued to ’62’, ’63’, ’65’, ’68’, ’69’ and ‘6A’. The values of SW2 not defined in tables 13 to 18 are RFU, except the values from ‘F0’ to ‘FF’ which are not defined in this part of ISO/IEC 7816.
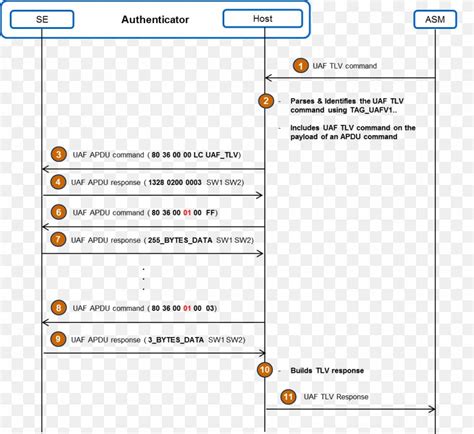
Provide a personal component to your applications and take advantage of the security of smart cards. Learn about the infrastructure, security mechanisms, and access conditions of this growing technology. In the context of smart cards, an application protocol data unit (APDU) is the communication unit between a smart card reader and a smart card. A command APDU is sent by the reader to the card — it contains a mandatory 4-byte header (CLA, INS, P1, P2) and from 0 to 65535 bytes of data. ISO 7816 part 4 annex A describes transportation of APDU messages by T=0 smart chip card protocol.
The response APDU has an optional body consisting of data and a mandatory trailer with two status bytes "SW1" and "SW2". SW1 and SW2 combined are the status word (SW). If the status word has the value 0x9000 (SW1 = 0x90, SW2=0x00), the .
EFTlab - Breakthrough Payment Technologies. Complete list of APDU responses. List of APDU responses for EMV processing with their description. . Note that the same list with extended searching options is implemented in our freeware BP-Tools product. . Missing any APDU response? Please let .
A command APDU is sent by the reader to the card – it contains a mandatory 4-byte header (CLA, INS, P1, P2) [2] and from 0 to 65 535 bytes of data. A response APDU is sent by the card to the reader – it contains from 0 to 65 536 bytes of data, and 2 mandatory status bytes (SW1, SW2).
In the context of smart cards, an Application Protocol Data Unit (APDU) is the unit of communication between a smart card reader and a smart card. The structure of the APDU is defined by ISO/IEC 7816-4, which specifies organization, security, and commands for .
When SW1 is neither E nor D, the card support the instruction. This part of ISO7816 does not interprets neither X SW1 bytes, nor SW2 bytes; Their meaning relates to the application itself. The end sequence SW1-SW2 gives the card status at the end of the command. Status Word (SW1, SW2): Consists of two bytes that provide information about the status of the operation (e.g., success, error, warnings). The status word codes are typically provided by the hardware manufacturer. Tables 13 to 18 specify values of SW2 when SW1 is valued to ’62’, ’63’, ’65’, ’68’, ’69’ and ‘6A’. The values of SW2 not defined in tables 13 to 18 are RFU, except the values from ‘F0’ to ‘FF’ which are not defined in this part of ISO/IEC 7816. Provide a personal component to your applications and take advantage of the security of smart cards. Learn about the infrastructure, security mechanisms, and access conditions of this growing technology.
In the context of smart cards, an application protocol data unit (APDU) is the communication unit between a smart card reader and a smart card. A command APDU is sent by the reader to the card — it contains a mandatory 4-byte header (CLA, INS, P1, P2) and from 0 to 65535 bytes of data.
ISO 7816 part 4 annex A describes transportation of APDU messages by T=0 smart chip card protocol.The response APDU has an optional body consisting of data and a mandatory trailer with two status bytes "SW1" and "SW2". SW1 and SW2 combined are the status word (SW). If the status word has the value 0x9000 (SW1 = 0x90, SW2=0x00), the .
$21.67
sw1 sw2 smart card|APDU (Application Protocol Data Unit)