nano rfid chip The Japanese giant Hitachi has developed the world’s smallest and thinnest Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) chip. Measuring only 0.15 x 0.15 millimeters in size and 7.5 micrometers thick, the wireless chip is a smaller version of the previous record holder – .
809. May 25, 2021. #2. Found this, but it pertains to reading. The watch can obviously send/trigger but I guess for payments only. iPhone has “reader mode” NFC that allows the users to passively read tags. This is what enables the shortcuts functionality. Reader mode isn’t a known feature of the watch and is not expected to be as Apple is .
0 · Smaller chips open door to new RFID applications
1 · Smaller Chips Open Door to New RFID Applications
2 · Hitachi Develops World’s Smallest RFID Chip
There are two popular RFID/NFC readers: RC522 and PN532 RFID/NFC reader. This tutorial focuses on RC522 RFID/NFC reader. PN532 RFID/NFC reader will be presented in an .
Researchers have made what is believed to be the smallest state-of-the-art . Researchers at North Carolina State University have made what is believed to .The Japanese giant Hitachi has developed the world’s smallest and thinnest Radio Frequency . Researchers have made what is believed to be the smallest state-of-the-art RFID chip, which should drive down the cost of RFID tags. In addition, the chip's design makes it possible to.
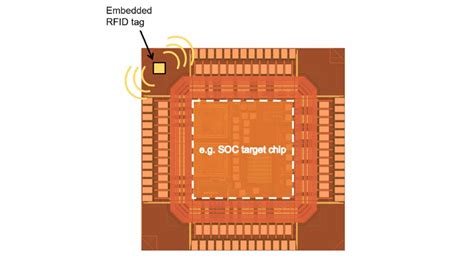
Researchers at North Carolina State University have made what is believed to be the smallest state-of-the-art RFID chip, which should drive down the cost of RFID tags. In addition, the chip’s design makes it possible to embed RFID tags into high value chips, such as computer chips, boosting supply chain security for high-end technologies.The Japanese giant Hitachi has developed the world’s smallest and thinnest Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) chip. Measuring only 0.15 x 0.15 millimeters in size and 7.5 micrometers thick, the wireless chip is a smaller version of the previous record holder – .
RFID sensor tags consist of an antenna, a radio frequency integrated circuit chip (RFIC), and at least one sensor. An ideal tag can communicate over a long distance and be seamlessly.Researchers at North Carolina State University have created what they say is the smallest-ever second-generation radio-frequency identification (RFID) chip — paving the way to lower-cost RFID tags and tags embeddable in new devices, including silicon chips. Radio frequency identification (RFid) tags are increasingly being used in electronic tagging, tracking and monitoring. Applications for RFid tags, benefits and drawbacks of using RFid tags, and industry applications for Nanobarcodes and ‘Senser’ tags are examined here. The application of the proposed magnetic metamaterial and local field enhancement package to near-field RFID technology, by offering high power transfer efficiency and a larger communication .
In particular, nanostructures related to the preparation of nano-inks and pastes for the printing of RFID tag's antennas, and features for data encoding through chipless chemical RFID transponders will be discussed.
Smaller chips open door to new RFID applications
The inkjet-printed RFID tag sensors based on polypyrrole, graphene, silver, copper and gold NPs, carbon nanotubes (CNTs), and other nanomaterials, which can be easily printed on flexible plastic, textile, paper, glass, and metallic surfaces are summarized. We demonstrate that a 25 \ (\upmu \) m wireless radio frequency identification (RFID) device can not only be taken up by a mammalian cell but can also be detected and specifically identified. Researchers have made what is believed to be the smallest state-of-the-art RFID chip, which should drive down the cost of RFID tags. In addition, the chip's design makes it possible to. Researchers at North Carolina State University have made what is believed to be the smallest state-of-the-art RFID chip, which should drive down the cost of RFID tags. In addition, the chip’s design makes it possible to embed RFID tags into high value chips, such as computer chips, boosting supply chain security for high-end technologies.
The Japanese giant Hitachi has developed the world’s smallest and thinnest Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) chip. Measuring only 0.15 x 0.15 millimeters in size and 7.5 micrometers thick, the wireless chip is a smaller version of the previous record holder – .
RFID sensor tags consist of an antenna, a radio frequency integrated circuit chip (RFIC), and at least one sensor. An ideal tag can communicate over a long distance and be seamlessly.
Researchers at North Carolina State University have created what they say is the smallest-ever second-generation radio-frequency identification (RFID) chip — paving the way to lower-cost RFID tags and tags embeddable in new devices, including silicon chips.
Smaller Chips Open Door to New RFID Applications
Hitachi Develops World’s Smallest RFID Chip
Radio frequency identification (RFid) tags are increasingly being used in electronic tagging, tracking and monitoring. Applications for RFid tags, benefits and drawbacks of using RFid tags, and industry applications for Nanobarcodes and ‘Senser’ tags are examined here. The application of the proposed magnetic metamaterial and local field enhancement package to near-field RFID technology, by offering high power transfer efficiency and a larger communication .
In particular, nanostructures related to the preparation of nano-inks and pastes for the printing of RFID tag's antennas, and features for data encoding through chipless chemical RFID transponders will be discussed.
The inkjet-printed RFID tag sensors based on polypyrrole, graphene, silver, copper and gold NPs, carbon nanotubes (CNTs), and other nanomaterials, which can be easily printed on flexible plastic, textile, paper, glass, and metallic surfaces are summarized.
contactless card tube station
contactless cards definition
*All payment plans are issued by Square Technologies, Inc. APR is 0%. First .
nano rfid chip|Smaller Chips Open Door to New RFID Applications