rfid systems architect Today’s RFID system architecture is carried over from the architecture used in other auto-id systems, chiefly optical barcode systems. As RFID introduces new functionalities and privacy risks, this classic architecture is no longer appropriate. How to use Quick Share: Find the file, photo, or content you want to share. Tap on the Share button. Select Quick Share. Your device will start looking for devices with Quick Share activated .
0 · types of rfid systems
1 · rfid schematic diagram
2 · rfid reader block diagram
3 · rfid radio frequency identification tags
4 · rfid radio frequency identification
5 · rfid full form in iot
6 · rfid full form in computer
7 · rfid block diagram
The M10 features a large 10.1-inch high-brightness, capacitive, multi-touch display that delivers speed and precision. Powered by a high-performance Intel processor with support for Microsoft Windows 10/11 and Linux Ubuntu, the .
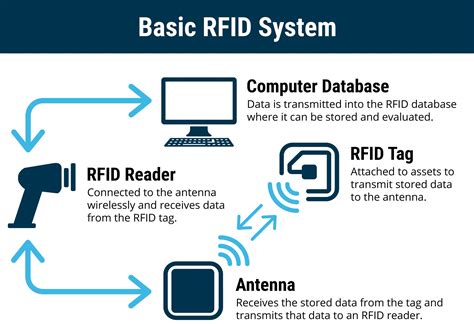
The RFID systems basically consist of three elements: a tag/transponder, a reader and a middleware deployed at a host computer. The RFID tag is a data carrier part of the RFID system which is placed on the objects to be uniquely identified.Today’s RFID system architecture is carried over from the architecture used in other auto-id systems, chiefly optical barcode systems. As RFID introduces new functionalities and privacy . The RFID systems basically consist of three elements: a tag/transponder, a reader and a middleware deployed at a host computer. The RFID tag is a data carrier part of the RFID system which is placed on the objects to be uniquely identified.Today’s RFID system architecture is carried over from the architecture used in other auto-id systems, chiefly optical barcode systems. As RFID introduces new functionalities and privacy risks, this classic architecture is no longer appropriate.
Techniques of RFID Systems: Architectures and Applications. From its first use in World War II, to differentiate between enemy and friendly aircraft, RFID has come to an era where it is used as an important identification tool, providing added security and .
Like RFID systems, these systems process terabytes of data, correct errors in real time, correlate events, detect patterns, re-organize and cleanse data and recover from faults—all in real time. RFID architectures should embrace three central principles of these systems. RFID systems are produced by many manufacturers and exist in countless variants. However, a RFID system consists mainly of three components; the transponder/tag, reader, and RFID middleware.
RFID System Architecture. RFID system architecture typically involves: Physical Layer: Tags, readers, and antennas. Network Layer: Connects readers to the backend system. Middleware: Filters, aggregates, and processes data from the readers. Application Layer: Interfaces with business applications for inventory management, access control, etc. The RFID middleware is a central point in the integration process of any RFID solution. There are several kinds of RFID tags and consequently several kinds of readers. This chapter describes the general architecture of such a middleware.
types of rfid systems
When designing an RFID-based application, a system architect must choose between three locations to store the information: a centralized database, a database locally attached to the device hold by each user of the application, or the tag itself.This paper presents an architecture design of a networked RFID tracking and tracing system, and also proposes a data schema design for managing track and trace data. Key Words: Radio Frequency Identification, Middleware, Track and Trace, Item .In Part IV, several major research challenges in the RFID field are presented, such unsatisfactory read accuracy even in the most favorable RF environments, low read ranges, security problems, localization of tags, energy harvesting and simulators and emulators for RFID systems.
The RFID systems basically consist of three elements: a tag/transponder, a reader and a middleware deployed at a host computer. The RFID tag is a data carrier part of the RFID system which is placed on the objects to be uniquely identified.
Today’s RFID system architecture is carried over from the architecture used in other auto-id systems, chiefly optical barcode systems. As RFID introduces new functionalities and privacy risks, this classic architecture is no longer appropriate.
Techniques of RFID Systems: Architectures and Applications. From its first use in World War II, to differentiate between enemy and friendly aircraft, RFID has come to an era where it is used as an important identification tool, providing added security and . Like RFID systems, these systems process terabytes of data, correct errors in real time, correlate events, detect patterns, re-organize and cleanse data and recover from faults—all in real time. RFID architectures should embrace three central principles of these systems. RFID systems are produced by many manufacturers and exist in countless variants. However, a RFID system consists mainly of three components; the transponder/tag, reader, and RFID middleware. RFID System Architecture. RFID system architecture typically involves: Physical Layer: Tags, readers, and antennas. Network Layer: Connects readers to the backend system. Middleware: Filters, aggregates, and processes data from the readers. Application Layer: Interfaces with business applications for inventory management, access control, etc.
The RFID middleware is a central point in the integration process of any RFID solution. There are several kinds of RFID tags and consequently several kinds of readers. This chapter describes the general architecture of such a middleware.When designing an RFID-based application, a system architect must choose between three locations to store the information: a centralized database, a database locally attached to the device hold by each user of the application, or the tag itself.This paper presents an architecture design of a networked RFID tracking and tracing system, and also proposes a data schema design for managing track and trace data. Key Words: Radio Frequency Identification, Middleware, Track and Trace, Item .
proximity card access control kit

free ip card access control software
1. Open your phone’s app store: Go to the app store on your smartphone. If you have an Android device, open the Google Play Store, and if you have an iPhone, open the App Store. 2. Search for an NFC reader app: In .
rfid systems architect|rfid full form in computer