high frequency rfid cards High Frequency RFID - Moderate speed communication: 424 kbit/s #3 - Write Capabilities. Most High Frequency RFID tags, including NFC tags, have data that can be read and re-written hundreds of times, but the same cannot be said for Low Frequency RFID tags. WEGL 91.1 FM is Auburn University's student-operated, student-funded radio station. WEGL's mission is to offer the Auburn community an entertaining and eclectic mix of music and free thought as only a non-commercial radio station .
0 · what frequency does rfid use
1 · ultra high frequency rfid tags
2 · ultra high frequency rfid reader
3 · rfid frequency chart
4 · low frequency rfid tags
5 · highfid radio frequency tags
6 · high frequency rfid tags
7 · disposable high frequency rfid tags
You can get a full set of BOTW-compatible Amiibo cards or mini cards for about $20 on .
Learn how to choose the right RFID frequency for your system with this step-by-step guide. . High Frequency RFID - Moderate speed communication: 424 kbit/s #3 - Write Capabilities. Most High Frequency RFID tags, including NFC tags, have data that can be read and re-written hundreds of times, but the same cannot be said for Low Frequency RFID tags.
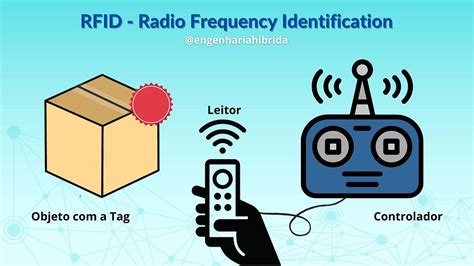
Learn how to choose the right RFID frequency for your system with this step-by-step guide. Explore the differences between LF, HF, and UHF, and optimize performance and cost for your RFID applications. High-frequency (HF) RFID tags: 3 to 30 MHz. HF RFID tags have longer read range and higher memory capabilities, making them well-suited to cataloging library media or for use in tracking bracelets for theme parks. Within the HF RFID category are a common type of smart label: Near field communication (NFC) tags. RFID operates across three primary frequency bands: Low Frequency (LF), High Frequency (HF), and Ultra-High Frequency (UHF). In this guide, we’ll explore the characteristics of each band, their applications, and how to choose the one that best fits your needs.High-Frequency (HF) RFID Cards. The operating frequency of high-frequency RFID cards is 13.56 MHz, and they are mainly used in payment systems, library management, public transportation, and other fields. High-frequency cards offer fast data .
This article will analyze in detail the characteristics and application differences of the three RFID frequencies: LF (low frequency), HF (high frequency), and UHF (ultra-high frequency).
High Frequency (HF) tags operate at 13.56 megahertz. They are essentially the ‘Swiss army knife of the RFID world. They have data transfer rates acceptable for many uses, a wide range of storing capacities and read distances ranging from millimeters to meters.
HF RFID, also known as High Frequency RFID, is the most widely used RFID technology with common applications including Access Control, Document Tracking and Ticketing due to its shorter read ranges up to 1 foot. The RFID cards use different frequency bands, including 125 kHz Low Frequency (LF), 13.56 MHz High Frequency (HF), and 860-960 Ultra-High Frequency (UHF). The frequency band of each card will determine its applications.High-frequency RFID operates at frequencies between 3 MHz and 30 MHz. This range offers longer reading distances, typically up to 1 meter. HF RFID is commonly used in applications such as library management, public transportation payment systems, and inventory tracking.
High Frequency RFID - Moderate speed communication: 424 kbit/s #3 - Write Capabilities. Most High Frequency RFID tags, including NFC tags, have data that can be read and re-written hundreds of times, but the same cannot be said for Low Frequency RFID tags.Learn how to choose the right RFID frequency for your system with this step-by-step guide. Explore the differences between LF, HF, and UHF, and optimize performance and cost for your RFID applications.
High-frequency (HF) RFID tags: 3 to 30 MHz. HF RFID tags have longer read range and higher memory capabilities, making them well-suited to cataloging library media or for use in tracking bracelets for theme parks. Within the HF RFID category are a common type of smart label: Near field communication (NFC) tags.
RFID operates across three primary frequency bands: Low Frequency (LF), High Frequency (HF), and Ultra-High Frequency (UHF). In this guide, we’ll explore the characteristics of each band, their applications, and how to choose the one that best fits your needs.High-Frequency (HF) RFID Cards. The operating frequency of high-frequency RFID cards is 13.56 MHz, and they are mainly used in payment systems, library management, public transportation, and other fields. High-frequency cards offer fast data .
This article will analyze in detail the characteristics and application differences of the three RFID frequencies: LF (low frequency), HF (high frequency), and UHF (ultra-high frequency). High Frequency (HF) tags operate at 13.56 megahertz. They are essentially the ‘Swiss army knife of the RFID world. They have data transfer rates acceptable for many uses, a wide range of storing capacities and read distances ranging from millimeters to meters.
HF RFID, also known as High Frequency RFID, is the most widely used RFID technology with common applications including Access Control, Document Tracking and Ticketing due to its shorter read ranges up to 1 foot. The RFID cards use different frequency bands, including 125 kHz Low Frequency (LF), 13.56 MHz High Frequency (HF), and 860-960 Ultra-High Frequency (UHF). The frequency band of each card will determine its applications.
what frequency does rfid use
ahmedabad brts student smart card form download
akasa electronic id smart card reader

Your Country Leader. WHEP. Radio Baldwin. Q-94. America's Best Country. WRWW. The Red Arrow Sports Network. Listen to Stream Auburn Tigers (Football) here on TuneIn! Listen .
high frequency rfid cards|high frequency rfid tags