test frequency of rfid tag Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) technology has revolutionised asset tracking systems, offering significant improvements in efficiency, accuracy, and cost-effectiveness. However, to fully leverage these benefits, it’s crucial to test and validate the performance of RFID tags thoroughly. Visa gift cards are available online. A gift anyone can appreciate. Choose from our selection of gift card designs or customize your own.
0 · what frequency does rfid use
1 · ultra high frequency rfid tags
2 · rfid radio frequency identification tags
3 · rfid radio frequency identification
4 · rfid frequency chart
5 · radio frequency identification tags are
6 · high frequency rfid tags
7 · disposable high frequency rfid tags
So eventually, I want to replace the NFC card with the Android device. This is my code for reading the ID from the card: TextView txt; NfcAdapter nfcAdapter; @Override. public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {. super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); setContentView(R.layout.activity_main); txt = (TextView) findViewById(R.id.textView);
Selecting the Right Frequency for RFID Tags: The appropriate RFID tag frequency is crucial for optimizing system performance and compatibility with reader equipment. Low-frequency (LF), High-frequency (HF), and Ultra-high Frequency (UHF) tags offer different read ranges, data . Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) technology has revolutionised asset .
Selecting the Right Frequency for RFID Tags: The appropriate RFID tag frequency is crucial for optimizing system performance and compatibility with reader equipment. Low-frequency (LF), High-frequency (HF), and Ultra-high Frequency (UHF) tags offer different read ranges, data transfer rates, and anti-collision capabilities suitable for various . Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) technology has revolutionised asset tracking systems, offering significant improvements in efficiency, accuracy, and cost-effectiveness. However, to fully leverage these benefits, it’s crucial to test and validate the performance of RFID tags thoroughly.
RFID-enhanced labels have specific properties based on the type of tags and the frequency on which they operate. We will review the frequencies and some of the behavioral properties of those tags in this post. During a typical two- to three-month pilot, a company can expect to improve its stock accuracy, comparing RFID-scanned results to what the ERP system shows for each location, once the tags are attached to merchandise and are being interrogated by employees. What Is the Maximum Read Range? The maximum read range is the longest distance the tag will send a detectable response signal under ideal laboratory test conditions, which includes the maximum strength query signal from the reader allowed by regulations. Generally, the bigger the tag, the longer the read range.The tag is usually rotated in 5-degree increments, enabling testers to ascertain the tag’s performance in various orientations to the reader antenna. By comparing the results of these measurements within the anechoic chamber, you can determine a new tag .
Common frequency bands for RFID tags include Low Frequency (LF), High Frequency (HF), and Ultra High Frequency (UHF). Each frequency band has its own advantages and limitations in terms of range, interference, and data transfer speed.
Tag test: Tag testing focuses on the performance of RFID tags in different materials, shapes, sizes, and harsh environments. Testers simulate actual usage scenarios to evaluate the performance indicators of tags such as reading rate, writing speed, durability (such as waterproof and heat resistance), and provide a scientific basis for tag .
Radio frequency identification (RFID) based on modulated backscatter is a wireless technology with a long history [1]. Various RFID systems use different frequency bands: low frequency (LF, 125-134 kHz), high frequency (HF, 13.56 MHz) and ultra-high frequency (UHF, 860-960 MHz). Passive RFID tags place unique requirements on the coding schemesused due to the impracticality of precision timing sources on board thetag, challenging bandwidth requirements, and the need for maximum RFpower transport to energize the tag.Selecting the Right Frequency for RFID Tags: The appropriate RFID tag frequency is crucial for optimizing system performance and compatibility with reader equipment. Low-frequency (LF), High-frequency (HF), and Ultra-high Frequency (UHF) tags offer different read ranges, data transfer rates, and anti-collision capabilities suitable for various . Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) technology has revolutionised asset tracking systems, offering significant improvements in efficiency, accuracy, and cost-effectiveness. However, to fully leverage these benefits, it’s crucial to test and validate the performance of RFID tags thoroughly.
RFID-enhanced labels have specific properties based on the type of tags and the frequency on which they operate. We will review the frequencies and some of the behavioral properties of those tags in this post. During a typical two- to three-month pilot, a company can expect to improve its stock accuracy, comparing RFID-scanned results to what the ERP system shows for each location, once the tags are attached to merchandise and are being interrogated by employees. What Is the Maximum Read Range? The maximum read range is the longest distance the tag will send a detectable response signal under ideal laboratory test conditions, which includes the maximum strength query signal from the reader allowed by regulations. Generally, the bigger the tag, the longer the read range.The tag is usually rotated in 5-degree increments, enabling testers to ascertain the tag’s performance in various orientations to the reader antenna. By comparing the results of these measurements within the anechoic chamber, you can determine a new tag .
Common frequency bands for RFID tags include Low Frequency (LF), High Frequency (HF), and Ultra High Frequency (UHF). Each frequency band has its own advantages and limitations in terms of range, interference, and data transfer speed.Tag test: Tag testing focuses on the performance of RFID tags in different materials, shapes, sizes, and harsh environments. Testers simulate actual usage scenarios to evaluate the performance indicators of tags such as reading rate, writing speed, durability (such as waterproof and heat resistance), and provide a scientific basis for tag .Radio frequency identification (RFID) based on modulated backscatter is a wireless technology with a long history [1]. Various RFID systems use different frequency bands: low frequency (LF, 125-134 kHz), high frequency (HF, 13.56 MHz) and ultra-high frequency (UHF, 860-960 MHz).
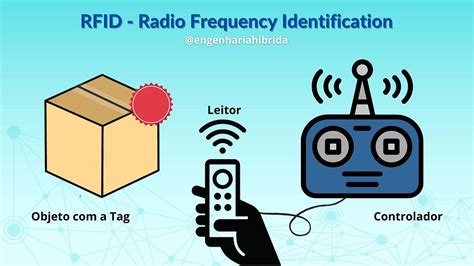
what frequency does rfid use
ultra high frequency rfid tags

rfid radio frequency identification tags
rfid radio frequency identification
rfid frequency chart
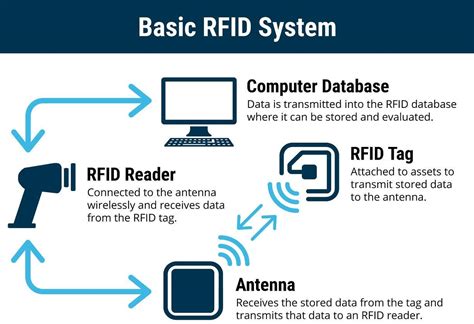
$8.99
test frequency of rfid tag|rfid radio frequency identification