passive hf rfid tags Discover the essentials of RFID passive tags, including their advantages, applications, and limitations. Learn how modern technology addresses these challenges and helps you make informed decisions for your RFID needs. The problems seems to be that it's not possible to emulate/modify the sector 0, .
0 · smallest passive rfid tag
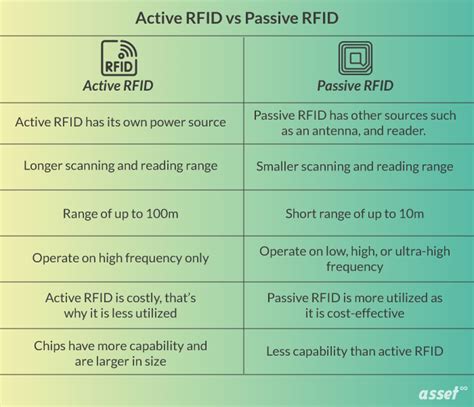
1 · rfid tags passive vs active
2 · rfid passive tag cost
3 · range of passive rfid tags
4 · passive rfid tags for sale
5 · passive rfid tag price
6 · passive rfid tag example
7 · long range passive rfid tags
The NFC21 Tools for Windows make managing NFC projects and writing NFC tags simple and intuitive. NFC21 Tools allows you to write NFC tags conveniently on your Windows PC. The software is available from Windows 7 .
Ultra-High Frequency (UHF): Operating between 300 MHz and 3 GHz, the primary range for . Passive RFID tags are ideal for short to medium-range applications, typically up .Ultra-High Frequency (UHF): Operating between 300 MHz and 3 GHz, the primary range for passive RFID tags is 860 to 960 MHz. UHF tags have a more extended read range, often several feet, and are commonly used in supply chain management and inventory tracking. Passive RFID tags are ideal for short to medium-range applications, typically up to a few feet. Within the category of passive RFID tags, there are further distinctions based on their operating frequency, including low-frequency (LF), high .
Discover the essentials of RFID passive tags, including their advantages, applications, and limitations. Learn how modern technology addresses these challenges and helps you make informed decisions for your RFID needs. Comparing ultra-high-frequency (UHF) vs. high-frequency (HF) vs. near field communication (NFC) vs. low-frequency (LF) RFID tag types. An explanation of the difference between active, passive and semi-passive RFID tags.
Passive RFID technology works by using radio waves to communicate between a tag and a reader. Unlike active tags, which require battery power, passive RFID tags do not require batteries and instead rely on radio waves emitted by the reader to power and transmit data.
This comprehensive guide delves into passive, active, UHF, HF, and NFC RFID tag types. It explores their applications, considerations for choosing the right tag, and key factors like read range, environmental conditions, and compatibility. Passive tags are widely favored for their affordability and versatility in diverse operational environments. Understanding the fundamental differences and advantages of active and passive RFID tags is crucial for implementing an effective RFID strategy tailored to specific business needs.Passive RFID—The Basics. Passive RFID Tags. Passive RFID tags contain a low-power integrated circuit (IC) attached to an antenna, and are enclosed with pro-tective packaging (like a plastic card) as determined by the application. On-board memory within the IC stores data.Types of RFID Tags & Labels. The most important distinction between RFID tag types is the way tags and readers communicate. Classifications include: Active RFID tags. Passive RFID tags (including RAIN RFID) Semi-passive RFID tags (also called battery-assisted passive, semi-active, or active/passive hybrid tags) Bluetooth low energy (BLE) systems.
Types of Passive RFID Tags. There are three primary frequency ranges used for passive RFID systems: Low Frequency (LF) 125 KHz to 136 KHz. Short Range Reading (contact – ~ 3”) Magnetic Coupling. Applications include Access Control, Key FOBs, Animal Tracking. High Frequency (HF) 13.56 MHz. Medium Range Reading (contact – ~ 10”) Magnetic Coupling.Ultra-High Frequency (UHF): Operating between 300 MHz and 3 GHz, the primary range for passive RFID tags is 860 to 960 MHz. UHF tags have a more extended read range, often several feet, and are commonly used in supply chain management and inventory tracking. Passive RFID tags are ideal for short to medium-range applications, typically up to a few feet. Within the category of passive RFID tags, there are further distinctions based on their operating frequency, including low-frequency (LF), high .Discover the essentials of RFID passive tags, including their advantages, applications, and limitations. Learn how modern technology addresses these challenges and helps you make informed decisions for your RFID needs.
Comparing ultra-high-frequency (UHF) vs. high-frequency (HF) vs. near field communication (NFC) vs. low-frequency (LF) RFID tag types. An explanation of the difference between active, passive and semi-passive RFID tags.
Passive RFID technology works by using radio waves to communicate between a tag and a reader. Unlike active tags, which require battery power, passive RFID tags do not require batteries and instead rely on radio waves emitted by the reader to power and transmit data. This comprehensive guide delves into passive, active, UHF, HF, and NFC RFID tag types. It explores their applications, considerations for choosing the right tag, and key factors like read range, environmental conditions, and compatibility. Passive tags are widely favored for their affordability and versatility in diverse operational environments. Understanding the fundamental differences and advantages of active and passive RFID tags is crucial for implementing an effective RFID strategy tailored to specific business needs.Passive RFID—The Basics. Passive RFID Tags. Passive RFID tags contain a low-power integrated circuit (IC) attached to an antenna, and are enclosed with pro-tective packaging (like a plastic card) as determined by the application. On-board memory within the IC stores data.
Types of RFID Tags & Labels. The most important distinction between RFID tag types is the way tags and readers communicate. Classifications include: Active RFID tags. Passive RFID tags (including RAIN RFID) Semi-passive RFID tags (also called battery-assisted passive, semi-active, or active/passive hybrid tags) Bluetooth low energy (BLE) systems.
asset tracking tags with rfid

smallest passive rfid tag
rfid tags passive vs active
You will need a rooted device and NFC Card Emulator Pro by Yuawnofei. It is a paid app .
passive hf rfid tags|passive rfid tag price