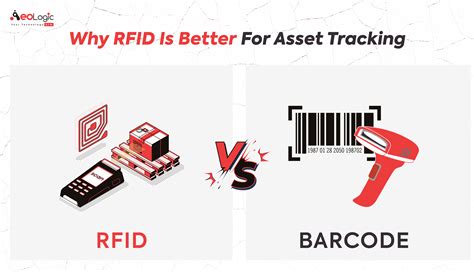
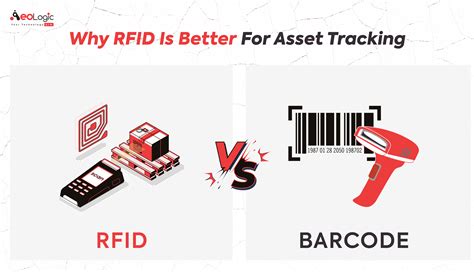
difference between rfid and barcode reader RFID uses radio waves to transmit data and does not require direct line-of-sight. Barcodes are optical and require a scanner aimed directly at the code on individual items. RFID is ideal for environments needing fast, automated data capture, while barcodes are cost-effective and widely used. $999.00
0 · rfid vs barcodes
1 · rfid vs barcode scanning
2 · rfid vs barcode in logistics
3 · rfid tags vs barcodes
4 · rfid tags pros and cons
5 · rfid chip pros and cons
6 · is rfid better than barcode
7 · barcode vs rfid comparison
Here, Hunter Cat NFC communicates with a passive tag, NFC smart card, or an NFC device operating in card emulation mode. It can read or write to a tag (although reading is a more common use-case because tags will often be .
If you are working with barcode but are still open to the possibility of investing in RFID in the future, how do you choose the right reader? We have . See more To understand the advantages and disadvantages of RFID, let’s take a closer look at some situations where it’s a better choice than barcoding. RFID is available in three main . Barcode readers work by using a beam of light to read the black and white pattern printed on the adhesive tag. On the other hand, RFID (or Radio-Frequency Identification) leverages radio waves to transmit data from RFID chips to the readers. To understand the advantages and disadvantages of RFID, let’s take a closer look at some situations where it’s a better choice than barcoding. RFID is available in three main types: low frequency (LF), high frequency (HF), and ultra-high frequency (UHF).
RFID uses radio waves to transmit data and does not require direct line-of-sight. Barcodes are optical and require a scanner aimed directly at the code on individual items. RFID is ideal for environments needing fast, automated data capture, while barcodes are cost-effective and widely used. Key Takeaways. RFID uses radio waves to automatically identify and track items, while barcodes require a scanner and direct line-of-sight. RFID technology offers a longer read range and higher data capacity than barcodes, which are . All barcodes represent data that is "read" by computers optically, with 1D barcodes usually using laser scanners and 2D barcodes requiring camera-based systems with image processing. What is RFID (and RAIN RFID)? RFID is a form of wireless communication that uses radio waves to identify and find objects. RFID uses radio waves to communicate data between a tag attached to an object and a reader. While barcodes require line-of-sight and individual scanning RFID can read multiple tags simultaneously and doesn’t need direct visibility.
RFID excels in logistics and large facility management, while barcodes are ideal for simpler tracking needs and retail inventory. Choosing between RFID and barcodes involves .(1)Batch Reading: RFID can read multiple tags simultaneously, greatly improving data collection efficiency. (2)No Line of Sight Required: RFID can read tag information without direct sight, suitable for complex warehousing and dense logistics environments.RFID technology surpasses barcode technology in recognition speed. RFID tags can be read at a faster rate, with multiple tags read simultaneously. RFID scanning is notably quicker, especially for bulk product movement, processing dozens of tags in a second.
RFID: Uses radio-frequency (RF) technology. Readers send a signal to the tag and read its response. Barcode: The foundational barcode system, mirroring today's UPC barcodes, was patented in the U.S. in 1952. RFID: Originated in the 1940s with roots in radar technology. Barcode readers work by using a beam of light to read the black and white pattern printed on the adhesive tag. On the other hand, RFID (or Radio-Frequency Identification) leverages radio waves to transmit data from RFID chips to the readers. To understand the advantages and disadvantages of RFID, let’s take a closer look at some situations where it’s a better choice than barcoding. RFID is available in three main types: low frequency (LF), high frequency (HF), and ultra-high frequency (UHF).
RFID uses radio waves to transmit data and does not require direct line-of-sight. Barcodes are optical and require a scanner aimed directly at the code on individual items. RFID is ideal for environments needing fast, automated data capture, while barcodes are cost-effective and widely used. Key Takeaways. RFID uses radio waves to automatically identify and track items, while barcodes require a scanner and direct line-of-sight. RFID technology offers a longer read range and higher data capacity than barcodes, which are . All barcodes represent data that is "read" by computers optically, with 1D barcodes usually using laser scanners and 2D barcodes requiring camera-based systems with image processing. What is RFID (and RAIN RFID)? RFID is a form of wireless communication that uses radio waves to identify and find objects. RFID uses radio waves to communicate data between a tag attached to an object and a reader. While barcodes require line-of-sight and individual scanning RFID can read multiple tags simultaneously and doesn’t need direct visibility.

rfid vs barcodes
RFID excels in logistics and large facility management, while barcodes are ideal for simpler tracking needs and retail inventory. Choosing between RFID and barcodes involves .(1)Batch Reading: RFID can read multiple tags simultaneously, greatly improving data collection efficiency. (2)No Line of Sight Required: RFID can read tag information without direct sight, suitable for complex warehousing and dense logistics environments.RFID technology surpasses barcode technology in recognition speed. RFID tags can be read at a faster rate, with multiple tags read simultaneously. RFID scanning is notably quicker, especially for bulk product movement, processing dozens of tags in a second.
nfc north standings 2022
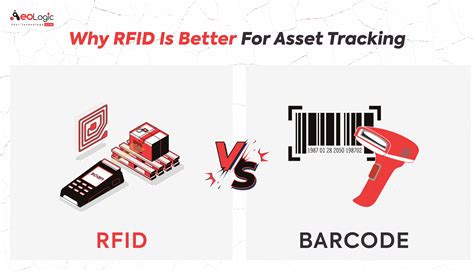
rfid vs barcode scanning
$16.50
difference between rfid and barcode reader|rfid tags pros and cons