epidermal passive rfid strain sensor for assisted technologies The epidermal strain gauge is battery-free (passive) and communicates wirelessly to an external reader using RFID technology. In this paper, we describe the testing of a UHF RFID tag in the form of a tongue proximity sensor to facilitate tongue control of a wheelchair or computer mouse communicating with a future reading system.
Build your own custom NFC card with our online tool. Total Price:$. Design Now. Upload Your File (s) Tell us any other special instructions for your order. Permission to Showcase. Give permission for us to promote and showcase .
0 · Miniaturized and Highly Sensitive Epidermal RFID Sensor for
1 · Epidermal Passive RFID Strain Sensor for Assisted Technologies
Hit the LOAD TAG button and select your Amiibo.bin dump file. Make sure any Amiibo are UNZIPPED you can put them all into their own folder called AMIIBO if you wish makes it easier. Click on WRITE TAG. Place your .
Miniaturized and Highly Sensitive Epidermal RFID Sensor for
An epidermal passive wireless strain sensor using radio frequency identification (RFID) tags is presented. The tag is intended to detect eyebrow or neck skin stretch where paraplegic . An epidermal passive wireless strain sensor using radio frequency identification (RFID) tags is presented. The tag is intended to detect eyebrow or neck skin stretch where .An electrically small (ES), epidermal radio frequency identification (RFID) tag is developed, which enables reliable human body temperature monitoring at a distance. It is based on the Huygens .An epidermal passive wireless strain sensor using radio frequency identification (RFID) tags is presented. The tag is intended to detect eyebrow or neck skin stretch where paraplegic patients have the capability to tweak facial muscles.
An epidermal passive wireless strain sensor using radio frequency identification (RFID) tags is presented. The tag is intended to detect eyebrow or neck skin stretch where paraplegic. The epidermal strain gauge is battery-free (passive) and communicates wirelessly to an external reader using RFID technology. In this paper, we describe the testing of a UHF RFID tag in the form of a tongue proximity sensor to facilitate tongue control of a wheelchair or computer mouse communicating with a future reading system.
can i write to nfc tags with my pc
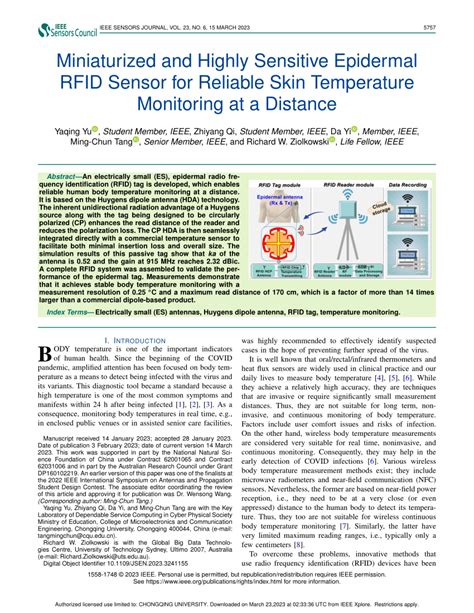
An electrically small (ES), epidermal radio frequency identification (RFID) tag is developed, which enables reliable human body temperature monitoring at a distance. It is based on the Huygens dipole antenna (HDA) technology.Epidermal Passive RFID Strain Sensor for Assisted Technologies. Osman O. Rakibet, Christina V. Rumens, John C. Batchelor, Senior Member IEEE and Simon J. Holder. Abstract—An epidermal passive wireless strain sensor using RFID tags is presented. An epidermal passive wireless strain sensor using radio frequency identification (RFID) tags is presented. The tag is intended to detect eyebrow or neck skin stretch where paraplegic.Epidermal Passive RFID Strain Sensor for Assisted Technologies. IEEE Antennas and Wireless Propagation Letters, 13, 814–817. doi:10.1109/lawp.2014.2318996
An epidermal passive wireless strain sensor using radio frequency identification (RFID) tags is presented. The tag is intended to detect eyebrow or neck skin stretch where paraplegic patients have the capability to tweak facial muscles. In this work, an epidermal passive RFID strain sensor on a flexible barium-titanate-loaded polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) substrate was used. Transmission-threshold power was used to interrogate the sensor, and strains of up to 10% were measured.
The specific application of passive, skin-mounted wireless sensing as an interface to assistive technologies will be discussed here through two prototype tags, one in the mouth and the other mounted externally on-skin.An epidermal passive wireless strain sensor using radio frequency identification (RFID) tags is presented. The tag is intended to detect eyebrow or neck skin stretch where paraplegic patients have the capability to tweak facial muscles. An epidermal passive wireless strain sensor using radio frequency identification (RFID) tags is presented. The tag is intended to detect eyebrow or neck skin stretch where paraplegic. The epidermal strain gauge is battery-free (passive) and communicates wirelessly to an external reader using RFID technology. In this paper, we describe the testing of a UHF RFID tag in the form of a tongue proximity sensor to facilitate tongue control of a wheelchair or computer mouse communicating with a future reading system.
An electrically small (ES), epidermal radio frequency identification (RFID) tag is developed, which enables reliable human body temperature monitoring at a distance. It is based on the Huygens dipole antenna (HDA) technology.
Epidermal Passive RFID Strain Sensor for Assisted Technologies. Osman O. Rakibet, Christina V. Rumens, John C. Batchelor, Senior Member IEEE and Simon J. Holder. Abstract—An epidermal passive wireless strain sensor using RFID tags is presented.
An epidermal passive wireless strain sensor using radio frequency identification (RFID) tags is presented. The tag is intended to detect eyebrow or neck skin stretch where paraplegic.Epidermal Passive RFID Strain Sensor for Assisted Technologies. IEEE Antennas and Wireless Propagation Letters, 13, 814–817. doi:10.1109/lawp.2014.2318996 An epidermal passive wireless strain sensor using radio frequency identification (RFID) tags is presented. The tag is intended to detect eyebrow or neck skin stretch where paraplegic patients have the capability to tweak facial muscles.
Epidermal Passive RFID Strain Sensor for Assisted Technologies
In this work, an epidermal passive RFID strain sensor on a flexible barium-titanate-loaded polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) substrate was used. Transmission-threshold power was used to interrogate the sensor, and strains of up to 10% were measured.

What do amiibo unlock? All amiibo provide a chance to unlock a wide variety of .
epidermal passive rfid strain sensor for assisted technologies|Epidermal Passive RFID Strain Sensor for Assisted Technologies