rfid tags coil antenna In a Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) application, an antenna coil is needed for two main reasons: To transmit the RF carrier signal to power up the tag. To receive data signals from . If you get your sheet cut professionally and have the cards cut reasonably (not too off-center), then the cards will be tournament legal. It is always up to the discretion of the head .
0 · rfid tag antenna types
1 · rfid scanning antenna
2 · rfid reader with antenna
3 · rfid directional antenna
4 · rfid antenna types
5 · rfid antenna size
6 · rfid antenna for sale
7 · rfid antenna design
The official source for NFL news, video highlights, fantasy football, game-day .
In a Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) application, an antenna coil is needed for two main reasons: To transmit the RF carrier signal to power up the tag. To receive data signals from .Passive RFID tags utilize an induced antenna coil voltage for operation. This induced AC voltage is rectified to provide a voltage source for the device. As the DC voltage reaches a certain level, the device starts operating.
In a Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) application, an antenna coil is needed for two main reasons: To transmit the RF carrier signal to power up the tag. To receive data signals from the tag. An RF signal can be radiated effectively if the linear dimension of the antenna is comparable with the wavelength of the operating frequency.The ST25 NFC (near field communication) and RFID (radio frequency identification) tags extract their power from the reader field. The tag and reader antennas are inductances mutually coupled by the magnetic field, similarly to a voltage transformer (see Figure 1).This method is based on eDesignSuite, a free on-line tool (available on www.st.com) featuring a calculation module that helps customers to design single-layer, rectangular coil antennas for NFC applications. Antenna tuning frequency adjustment and .This paper describes the design steps for creating and tuning an NFC/high frequency (HF) RFID antenna tuned to 13.56 MHz for the TRF79xxA series of devices. The matching network uses a 50-Ω 3-element match. A 3-element match is recommended as it allows the designer to select the required antenna quality factor (Q) for the application. Contents.
LF RFID at 125 kHz uses magnetic fields to power tags and load modulation to communicate with them. Your reader does not appear to be powerful enough to generate a magnetic field that has sufficient strength.
RFID tags extract all of their power to both operate and communicate from the reader’s magnetic field. Coupling between the tag and reader is via the mutual inductance of the two loop antennas, see Figure 1.
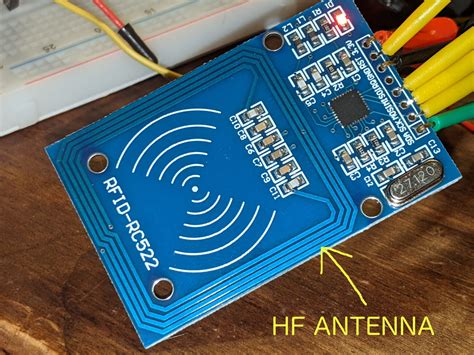
While RFID accomplishes the same functionality of a barcode or magnetic strip on a credit card, it has some unique use cases that make it worth learning about and designing. In this blog, we’ll be covering how RFID works and how .The tag is composed of an antenna coil and a silicon chip that includes basic modulation circuitry and non-volatile memory. The tag is energized by a time-varying electromagnetic radio frequency (RF) wave that is transmitted by the reader. This RF signal is called a carrier signal.Coilcraft transponder coils are wirewound, surface mount antennas designed for use in a 125 kHz RFID system. They are rated for 125°C operation. Doc 397. Explore the role of transponder coils in RFID systems. With Coilcraft, learn how coil inductance affects sensitivity and read distance for optimal performance.
Passive RFID tags utilize an induced antenna coil voltage for operation. This induced AC voltage is rectified to provide a voltage source for the device. As the DC voltage reaches a certain level, the device starts operating.In a Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) application, an antenna coil is needed for two main reasons: To transmit the RF carrier signal to power up the tag. To receive data signals from the tag. An RF signal can be radiated effectively if the linear dimension of the antenna is comparable with the wavelength of the operating frequency.
The ST25 NFC (near field communication) and RFID (radio frequency identification) tags extract their power from the reader field. The tag and reader antennas are inductances mutually coupled by the magnetic field, similarly to a voltage transformer (see Figure 1).
This method is based on eDesignSuite, a free on-line tool (available on www.st.com) featuring a calculation module that helps customers to design single-layer, rectangular coil antennas for NFC applications. Antenna tuning frequency adjustment and .This paper describes the design steps for creating and tuning an NFC/high frequency (HF) RFID antenna tuned to 13.56 MHz for the TRF79xxA series of devices. The matching network uses a 50-Ω 3-element match. A 3-element match is recommended as it allows the designer to select the required antenna quality factor (Q) for the application. Contents.
LF RFID at 125 kHz uses magnetic fields to power tags and load modulation to communicate with them. Your reader does not appear to be powerful enough to generate a magnetic field that has sufficient strength.RFID tags extract all of their power to both operate and communicate from the reader’s magnetic field. Coupling between the tag and reader is via the mutual inductance of the two loop antennas, see Figure 1.
While RFID accomplishes the same functionality of a barcode or magnetic strip on a credit card, it has some unique use cases that make it worth learning about and designing. In this blog, we’ll be covering how RFID works and how .The tag is composed of an antenna coil and a silicon chip that includes basic modulation circuitry and non-volatile memory. The tag is energized by a time-varying electromagnetic radio frequency (RF) wave that is transmitted by the reader. This RF signal is called a carrier signal.
rfid tag antenna types

azure ad smart card
birmingham smart card
The facts and figures surrounding paper business cards aren’t pretty. Many .
rfid tags coil antenna|rfid scanning antenna