zigbee rfid sensor For RFID-RTLS applications, ZigBee sensors are deployed with sufficient density to “cover” a building (or possibly some subset of a building). This coverage also provides a sufficient . This means that door keycards could be copied, or data on any other NFC payment chip could be cloned onto an Android device if the attacker's phone gets within NFC .
0 · rfid sensors
1 · rfid iot sensing
2 · rfid and iot sensor
3 · mdpi rfid testing
The wild card races were far from finished, but slip-ups from the New York Jets, Pittsburgh Steelers, Atlanta Falcons or one of the teams at the top of the NFC North were the .
greater anglia smart card help
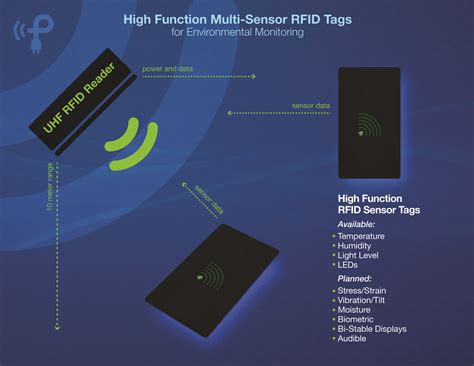
Passive RFID sensors harvest the RF energy from RF radiation to power the circuit, perform the sensing task, and save the data in the RFID chip to be accessed by RFID .Order Article Reprints. Journal: Sensors, 2020 Volume: 20 Number: 2495 Article: .
Create a SciFeed alert for new publications. With following keywords. passive sensorsAction Date Notes Link; article xml file uploaded: 28 April 2020 14:34 CEST: .For RFID-RTLS applications, ZigBee sensors are deployed with sufficient density to “cover” a building (or possibly some subset of a building). This coverage also provides a sufficient . RFID and wireless sensor networks (WSN) are both important technologies in the IoT domain. RFID can only be used for object identification, but WSNs serve a far greater .
gt08 bluetooth smart watch with sim card slot review
Radio frequency identification (RFID) and wireless sensors networks (WSNs) are two fundamental pillars that enable the Internet of Things (IoT). RFID systems are able to . ZigBee and radio frequency identification (RFID) are two wireless technologies that have each developed hosts of applications independent of each other. Each has benefits, with .find detailed coverage of state-of-the-art RFID/sensor technology such as inkjet printing and low-cost flexible substrates as well as a discussion of certain worldwide applications. Contents .The ability of a sensor network node in storing and transmitting a unique identifier enables it to work as a RFID sensor node. A RFID sen-sor node uses IEEE 802.15.4 or Zigbee to .
We propose an innovative radio-switched Zigbee network, where remote sensor nodes are selectively turned off. More precisely, the radio control is based on the use of radio . Zigbee is one of the most exciting wireless sensor network (WSN) technologies for monitoring and control. In our previous research, an integrated Zigbee RFID sensor network .
Passive RFID sensors harvest the RF energy from RF radiation to power the circuit, perform the sensing task, and save the data in the RFID chip to be accessed by RFID readers. Both analog and digital RFID sensing can provide a variety of . Zigbee sends instructions between smart home devices, from a smart speaker to a light bulb, for example, or from a switch to a bulb – without first going via a central control hub, like a Wi-Fi.For RFID-RTLS applications, ZigBee sensors are deployed with sufficient density to “cover” a building (or possibly some subset of a building). This coverage also provides a sufficient density of network nodes for routing data, even at low transmission power. With the sensors themselves providing the backbone for wirelessly collecting sensor RFID and wireless sensor networks (WSN) are both important technologies in the IoT domain. RFID can only be used for object identification, but WSNs serve a far greater purpose. The two are very different but merging them has many advantages.
Radio frequency identification (RFID) and wireless sensors networks (WSNs) are two fundamental pillars that enable the Internet of Things (IoT). RFID systems are able to identify and track. ZigBee and radio frequency identification (RFID) are two wireless technologies that have each developed hosts of applications independent of each other. Each has benefits, with ZigBee supporting advanced sensor networks and RFID suitable for low-power wireless tracking of people and objects.
find detailed coverage of state-of-the-art RFID/sensor technology such as inkjet printing and low-cost flexible substrates as well as a discussion of certain worldwide applications. Contents overview:
The ability of a sensor network node in storing and transmitting a unique identifier enables it to work as a RFID sensor node. A RFID sen-sor node uses IEEE 802.15.4 or Zigbee to communicate with a sensor gateway. Passive or semi-active RFID tags use inductive/propagation coupling to communicate with readers. We propose an innovative radio-switched Zigbee network, where remote sensor nodes are selectively turned off. More precisely, the radio control is based on the use of radio frequency identification (RFID) technology, leading to a hybrid Zigbee/RFID architecture. In other words, we consider two logically overlapped networks, RFID and Zigbee. Zigbee is one of the most exciting wireless sensor network (WSN) technologies for monitoring and control. In our previous research, an integrated Zigbee RFID sensor network was designed as an `all-in-one' system solution for Humanitarian . Passive RFID sensors harvest the RF energy from RF radiation to power the circuit, perform the sensing task, and save the data in the RFID chip to be accessed by RFID readers. Both analog and digital RFID sensing can provide a variety of .
Zigbee sends instructions between smart home devices, from a smart speaker to a light bulb, for example, or from a switch to a bulb – without first going via a central control hub, like a Wi-Fi.For RFID-RTLS applications, ZigBee sensors are deployed with sufficient density to “cover” a building (or possibly some subset of a building). This coverage also provides a sufficient density of network nodes for routing data, even at low transmission power. With the sensors themselves providing the backbone for wirelessly collecting sensor RFID and wireless sensor networks (WSN) are both important technologies in the IoT domain. RFID can only be used for object identification, but WSNs serve a far greater purpose. The two are very different but merging them has many advantages.
Radio frequency identification (RFID) and wireless sensors networks (WSNs) are two fundamental pillars that enable the Internet of Things (IoT). RFID systems are able to identify and track. ZigBee and radio frequency identification (RFID) are two wireless technologies that have each developed hosts of applications independent of each other. Each has benefits, with ZigBee supporting advanced sensor networks and RFID suitable for low-power wireless tracking of people and objects.
find detailed coverage of state-of-the-art RFID/sensor technology such as inkjet printing and low-cost flexible substrates as well as a discussion of certain worldwide applications. Contents overview:The ability of a sensor network node in storing and transmitting a unique identifier enables it to work as a RFID sensor node. A RFID sen-sor node uses IEEE 802.15.4 or Zigbee to communicate with a sensor gateway. Passive or semi-active RFID tags use inductive/propagation coupling to communicate with readers. We propose an innovative radio-switched Zigbee network, where remote sensor nodes are selectively turned off. More precisely, the radio control is based on the use of radio frequency identification (RFID) technology, leading to a hybrid Zigbee/RFID architecture. In other words, we consider two logically overlapped networks, RFID and Zigbee.
rfid sensors
rfid iot sensing
rfid and iot sensor
$14.20Edit: Please read both answers submitted by henrycjc and me for a full explaination. Where do I find the documentation to use in android.nfc.tech.NfcA? /** * Provides access to NFC-A (ISO 14443-3A) .
zigbee rfid sensor|rfid sensors