rfid based indoor positioning system Unlike other RFID-based localization systems, Saab et al. proposed a novel RFID-based methodology which employs a single nonsteered stationary antenna and three passive tags mounted on each object to estimate the location and orientation of objects. Paragon ID NFC inlays. The Tracker range is designed for industrial applications requiring high read range and is based on NFC type 5 IC’s. The Guardian range is designed for short read .
0 · rfid tags for location detection
1 · rfid positioning system
2 · rfid position tracking system
3 · rfid position tracking
4 · rfid placement
5 · rfid map
6 · rfid localization
7 · rfid indoor positioning
The affiliates list also includes the renewal of stations in major markets of Birmingham, Huntsville, Montgomery, Mobile and Columbus, Georgia. . Tiger Talk, Auburn's .
Unlike other RFID-based localization systems, Saab et al. proposed a novel RFID-based methodology which employs a single nonsteered stationary antenna and three passive tags mounted on each object to estimate the . Unlike other RFID-based localization systems, Saab et al. proposed a novel RFID-based methodology which employs a single nonsteered stationary antenna and three passive tags mounted on each object to estimate the location and orientation of objects.
This study offers a new approach to real-time indoor positioning using passive RFID technology to estimate the real-time location of smart home users based on their movements in smart environment space. In this paper, indoor location technology based on RFID is selected, and several commonly used location algorithms are introduced in detail. Combined with the latest research, several improved RFID positioning systems are summarized, which improve positioning accuracy and .
Radio-based indoor positioning systems. Use radio waves to locate and track objects or people inside buildings. These systems are designed specifically for indoor environments. Here’s a look at the main types of radio-based positioning systems commonly used: RFID, BLE, UWB, and Wi-Fi. 1. RFID (Radio-Frequency Identification)However, the performance of the Global Positioning System (GPS) substantially deteriorates when applied in indoor scenarios, attributed to the intricate interplay of multipath reflections and the pronounced signal attenuation stemming from obstructions introduced by adjacent structures and the complex indoor surroundings [3, 4].
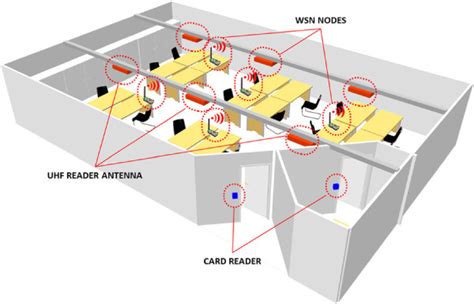
Indoor positioning of objects and people is becoming of great importance in the Internet of Things (IoT), in-home automation, and navigation in malls, airports, or very large buildings. Positioning is determined by multiple distance measurements between reference points and sensors.In this paper, a dual-channel low-power passive RFID positioning system is proposed to solve this problem. The probability for accurately locating a target within 0.5 m from its real position can reach 96.7% in this system.
1 Introduction. With the continual advancement of mobile communication technology [], location-based services (LBS) have become integral to the daily lives of individuals, improving both living and working experiences.Despite the utility of the global positioning system (GPS) for determining locations in a 2D reference frame, its effectiveness is hindered in areas without .
Radio Frequency Identification (RFID), which uses radio waves to wirelessly transmit the identity (e.g. a unique serial number) and other information of an object, is an emerging technology for indoor positioning (Ahuja & Potti 2010).Several advantages of Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) Technology, such as anti-interference, small, light and portable size of RFID tags, and its unique identification of different objects, make it superior to other wireless communication technologies for indoor positioning. Unlike other RFID-based localization systems, Saab et al. proposed a novel RFID-based methodology which employs a single nonsteered stationary antenna and three passive tags mounted on each object to estimate the location and orientation of objects. This study offers a new approach to real-time indoor positioning using passive RFID technology to estimate the real-time location of smart home users based on their movements in smart environment space.
In this paper, indoor location technology based on RFID is selected, and several commonly used location algorithms are introduced in detail. Combined with the latest research, several improved RFID positioning systems are summarized, which improve positioning accuracy and .

advantages of rfid tag
rfid tags for location detection
Radio-based indoor positioning systems. Use radio waves to locate and track objects or people inside buildings. These systems are designed specifically for indoor environments. Here’s a look at the main types of radio-based positioning systems commonly used: RFID, BLE, UWB, and Wi-Fi. 1. RFID (Radio-Frequency Identification)However, the performance of the Global Positioning System (GPS) substantially deteriorates when applied in indoor scenarios, attributed to the intricate interplay of multipath reflections and the pronounced signal attenuation stemming from obstructions introduced by adjacent structures and the complex indoor surroundings [3, 4].
Indoor positioning of objects and people is becoming of great importance in the Internet of Things (IoT), in-home automation, and navigation in malls, airports, or very large buildings. Positioning is determined by multiple distance measurements between reference points and sensors.In this paper, a dual-channel low-power passive RFID positioning system is proposed to solve this problem. The probability for accurately locating a target within 0.5 m from its real position can reach 96.7% in this system. 1 Introduction. With the continual advancement of mobile communication technology [], location-based services (LBS) have become integral to the daily lives of individuals, improving both living and working experiences.Despite the utility of the global positioning system (GPS) for determining locations in a 2D reference frame, its effectiveness is hindered in areas without .
Radio Frequency Identification (RFID), which uses radio waves to wirelessly transmit the identity (e.g. a unique serial number) and other information of an object, is an emerging technology for indoor positioning (Ahuja & Potti 2010).
rfid positioning system
active semi passive and passive rfid tags

Listen to Auburn Football on TuneIn. Plus, fuel your fandom with local and national sports talk, pregame and postgame analysis, all your favorite sports podcasts, and live coverage of the .
rfid based indoor positioning system|rfid position tracking