smart card blake hash Released in January 2020, BLAKE3 is a cryptographic hash function that is both faster and more parallelizable than its predecessor, BLAKE2. It’s designed to be used in a . Transit passes often take the form of cards, whether they be swipe or NFC (Near Field Communication). They are thin, but unless you wear them like a badge around your neck they are easy to lose in a pocket and clumsy to fish .
0 · blake hashing
1 · blake hash function
2 · blake 256 hash function
Yubico - Security Key C NFC - Black- Two-Factor authentication (2FA) Security Key, Connect via USB-C or NFC, FIDO U2F/FIDO2 Certified. . The Cryptnox .
In this paper we present an attack to the BLOKE and BRAKE hash functions, which are weakened versions of the SHA-3 candidate BLAKE. In difference to BLAKE, the BLOKE hash function . Released in January 2020, BLAKE3 is a cryptographic hash function that is both faster and more parallelizable than its predecessor, BLAKE2. It’s designed to be used in a .Prominent examples include RFID tags and cryp-tographic smart-cards. In order to estimate the suitability of some promis-ing SHA-3 candidates, we have implemented ARIRANG, BLAKE, . BLAKE3 was designed to be as secure as BLAKE2, yet considerably faster, thanks to 1) a compression function with a reduced number of rounds, and 2) a tree-based mode .
3.1 Integrity: Hashing Concept. To validate the integrity of the data transmitted over the channel, message authentication code (MAC) is used for checking the messages and the .
The BLAKE2s variant is optimized for 8- to 32-bit platforms and has significantly smaller implementation footprint than any other secure cryptographic hash function. We expect to see . Keyed hashing (HMAC) with Blake2. Keyed hashing can be used to apply a secret key onto a hash and can thus be used for authentication of a message and generate a MAC .This is a comprehensive description of the cryptographic hash function BLAKE, one of the five final contenders in the NIST SHA3 competition, and of BLAKE2, an improved version popular .
The cryptographic hash function BLAKE Animation overview/visualization of how the hash function worksOriginally here: www.youtube.com/watch?v=PgpJNRnx6eYnot .
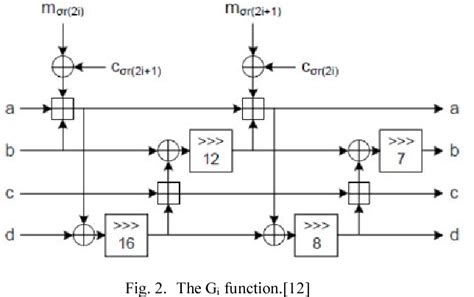
BLAKE is a cryptographic hash function based on Daniel J. Bernstein's ChaCha stream cipher, but a permuted copy of the input block, XORed with round constants, is added before each ChaCha round. Like SHA-2, there are two variants differing in the word size. ChaCha operates on a 4×4 array of words.In this paper we present an attack to the BLOKE and BRAKE hash functions, which are weakened versions of the SHA-3 candidate BLAKE. In difference to BLAKE, the BLOKE hash function does not permute the message words and constants in the round computation . Released in January 2020, BLAKE3 is a cryptographic hash function that is both faster and more parallelizable than its predecessor, BLAKE2. It’s designed to be used in a wide range of applications, including hashing files in version control systems, deriving keys in password managers, and even pseudorandom number generation.Prominent examples include RFID tags and cryp-tographic smart-cards. In order to estimate the suitability of some promis-ing SHA-3 candidates, we have implemented ARIRANG, BLAKE, Grøstl, and Skein in hardware with the main em-phasis on the reduction of .
BLAKE3 was designed to be as secure as BLAKE2, yet considerably faster, thanks to 1) a compression function with a reduced number of rounds, and 2) a tree-based mode allowing implementations to leverage parallel processing. 3.1 Integrity: Hashing Concept. To validate the integrity of the data transmitted over the channel, message authentication code (MAC) is used for checking the messages and the authentication, ensuring that the integrity of the information has .The BLAKE2s variant is optimized for 8- to 32-bit platforms and has significantly smaller implementation footprint than any other secure cryptographic hash function. We expect to see it used in embedded, smart card, and Internet of Things (IoT) security applications. Keyed hashing (HMAC) with Blake2. Keyed hashing can be used to apply a secret key onto a hash and can thus be used for authentication of a message and generate a MAC (Message Authentication.
This is a comprehensive description of the cryptographic hash function BLAKE, one of the five final contenders in the NIST SHA3 competition, and of BLAKE2, an improved version popular among developers.
blake hashing
blake hash function
The cryptographic hash function BLAKE Animation overview/visualization of how the hash function worksOriginally here: www.youtube.com/watch?v=PgpJNRnx6eYnot .
BLAKE is a cryptographic hash function based on Daniel J. Bernstein's ChaCha stream cipher, but a permuted copy of the input block, XORed with round constants, is added before each ChaCha round. Like SHA-2, there are two variants differing in the word size. ChaCha operates on a 4×4 array of words.
In this paper we present an attack to the BLOKE and BRAKE hash functions, which are weakened versions of the SHA-3 candidate BLAKE. In difference to BLAKE, the BLOKE hash function does not permute the message words and constants in the round computation .
Released in January 2020, BLAKE3 is a cryptographic hash function that is both faster and more parallelizable than its predecessor, BLAKE2. It’s designed to be used in a wide range of applications, including hashing files in version control systems, deriving keys in password managers, and even pseudorandom number generation.
Prominent examples include RFID tags and cryp-tographic smart-cards. In order to estimate the suitability of some promis-ing SHA-3 candidates, we have implemented ARIRANG, BLAKE, Grøstl, and Skein in hardware with the main em-phasis on the reduction of . BLAKE3 was designed to be as secure as BLAKE2, yet considerably faster, thanks to 1) a compression function with a reduced number of rounds, and 2) a tree-based mode allowing implementations to leverage parallel processing. 3.1 Integrity: Hashing Concept. To validate the integrity of the data transmitted over the channel, message authentication code (MAC) is used for checking the messages and the authentication, ensuring that the integrity of the information has .The BLAKE2s variant is optimized for 8- to 32-bit platforms and has significantly smaller implementation footprint than any other secure cryptographic hash function. We expect to see it used in embedded, smart card, and Internet of Things (IoT) security applications.
Keyed hashing (HMAC) with Blake2. Keyed hashing can be used to apply a secret key onto a hash and can thus be used for authentication of a message and generate a MAC (Message Authentication.This is a comprehensive description of the cryptographic hash function BLAKE, one of the five final contenders in the NIST SHA3 competition, and of BLAKE2, an improved version popular among developers.

blake 256 hash function
A Magic card is a card that allows you to change its UID. Generally, NFC cards .
smart card blake hash|blake hashing