rfid tags frequency Unlike RF tags, RFID tags tend to work over much shorter distances. Some actually have to be held right next to a reader device, while others operate at a distance of 10cm (4 inches) or less. Simple RFID tags are described as passive. Product Description. ACR1251U USB NFC Reader II offers advanced features such as .There can be several factors contributing to an NFC read error, including technical issues with the NFC-enabled device, compatibility problems between the device and the NFC tag, environmental interference, or physical .
0 · what frequency does rfid use
1 · ultra high frequency rfid tags
2 · rfid radio frequency identification tags
3 · rfid radio frequency identification
4 · rfid frequency chart
5 · radio frequency identification tags are
6 · high frequency rfid tags
7 · disposable high frequency rfid tags
NFC_reader.py This file contains bidirectional Unicode text that may be .
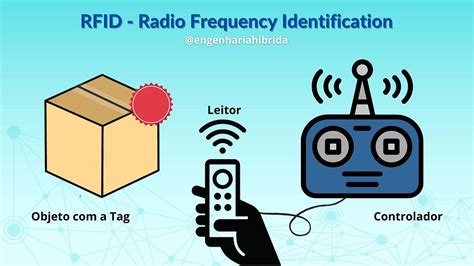
RFID (radio frequency identification) is a form of wireless communication that incorporates the use of electromagnetic or electrostatic coupling in the radio frequency portion of the .
enter smart card says network path was not found
Radio-frequency identification (RFID) uses electromagnetic fields to automatically identify and track tags attached to objects. An RFID system consists of a tiny radio transponder called a tag, a radio receiver, and a transmitter.RFID (radio frequency identification) is a form of wireless communication that incorporates the use of electromagnetic or electrostatic coupling in the radio frequency portion of the electromagnetic spectrum to uniquely identify an object, animal or person.RFID tags are categorized according to the frequency at which they are designed to operate. Four primary frequency ranges are allocated by various government authorities for use by RFID systems. • Low frequency (LF) • High frequency (HF) • Ultra high frequency (UHF) • Microwave frequency (microwave)
Unlike RF tags, RFID tags tend to work over much shorter distances. Some actually have to be held right next to a reader device, while others operate at a distance of 10cm (4 inches) or less. Simple RFID tags are described as passive.Learn how to choose the right RFID frequency for your system with this step-by-step guide. Explore the differences between LF, HF, and UHF, and optimize performance and cost for your RFID applications. Frequency bands: RFID tags operate in different frequency bands, such as low frequency (LF: 125 kHz and 134 kHz), high frequency (HF: 13.56 MHz), and ultra-high frequency (UHF: 860-960 MHz). Each frequency band has its advantages in terms of read range, data transfer speed, and resistance to interference.
There are a variety of RFID tags on the market today, differentiated by frequency range (low, high and ultra-high). Each RFID type can be either active (powered), passive (un-powered) or semi-passive (battery-assisted). Low-frequency (LF) RFID tags: 30 KHz to 300 KHz.
radio-frequency identification (RFID), method of wireless communication that uses electromagnetic waves to identify and track tags attached to objects, people, or animals. The attached tags, called RFID tags, store digitally encoded data that can be read by an RFID reader.
The operating frequency of high frequency RFID tags (mainly 13.56 MHz) generally ranges from 3 MHz to 30 MHz. The global uniform frequency of the HF tag makes it suitable for a variety of RFID applications, especially in scenarios that require medium-range reading. Power supply, read range, and multi-tag capability.
The most common RFID frequencies used for RFID applications are: Low frequency (9-135 KHz) High frequency (13.553-15.567 MHz) Amateur radio band (430-440 MHz) Ultra-high frequency (860-930 MHz) Microwave (2.4-2.4835 GHz, 5.8 GHz)Radio-frequency identification (RFID) uses electromagnetic fields to automatically identify and track tags attached to objects. An RFID system consists of a tiny radio transponder called a tag, a radio receiver, and a transmitter.RFID (radio frequency identification) is a form of wireless communication that incorporates the use of electromagnetic or electrostatic coupling in the radio frequency portion of the electromagnetic spectrum to uniquely identify an object, animal or person.
RFID tags are categorized according to the frequency at which they are designed to operate. Four primary frequency ranges are allocated by various government authorities for use by RFID systems. • Low frequency (LF) • High frequency (HF) • Ultra high frequency (UHF) • Microwave frequency (microwave) Unlike RF tags, RFID tags tend to work over much shorter distances. Some actually have to be held right next to a reader device, while others operate at a distance of 10cm (4 inches) or less. Simple RFID tags are described as passive.
Learn how to choose the right RFID frequency for your system with this step-by-step guide. Explore the differences between LF, HF, and UHF, and optimize performance and cost for your RFID applications. Frequency bands: RFID tags operate in different frequency bands, such as low frequency (LF: 125 kHz and 134 kHz), high frequency (HF: 13.56 MHz), and ultra-high frequency (UHF: 860-960 MHz). Each frequency band has its advantages in terms of read range, data transfer speed, and resistance to interference. There are a variety of RFID tags on the market today, differentiated by frequency range (low, high and ultra-high). Each RFID type can be either active (powered), passive (un-powered) or semi-passive (battery-assisted). Low-frequency (LF) RFID tags: 30 KHz to 300 KHz.radio-frequency identification (RFID), method of wireless communication that uses electromagnetic waves to identify and track tags attached to objects, people, or animals. The attached tags, called RFID tags, store digitally encoded data that can be read by an RFID reader.
The operating frequency of high frequency RFID tags (mainly 13.56 MHz) generally ranges from 3 MHz to 30 MHz. The global uniform frequency of the HF tag makes it suitable for a variety of RFID applications, especially in scenarios that require medium-range reading. Power supply, read range, and multi-tag capability.
what frequency does rfid use
ultra high frequency rfid tags
Scan this QR code to download the app now. Or check it out in the app stores . Could there be a way to scan amiibos without buying an nfc reader on o3ds models via cfw .
rfid tags frequency|disposable high frequency rfid tags