lf hf uhf rfid Typically, passive RFID systems use either low frequency (LF), high frequency (HF), or ultra-high frequency (UHF). Based on a schematic overview, this blog article provides an initial guide to these frequency ranges and their characteristics. After learning about how this technology works, perhaps contactless credit cards seem a little too easy to be safe. See more
0 · rfid vs hf
1 · rfid range
2 · rfid frequency
3 · lf hf uhf range
4 · lf hf uhf
5 · high frequency rfid range
6 · high frequency rfid chart
7 · high frequency rfid
1. Open your phone’s app store: Go to the app store on your smartphone. If you have an Android device, open the Google Play Store, and if you have an iPhone, open the App Store. 2. Search for an NFC reader app: In the app store’s search bar, type in “NFC reader” or .
RFID operates across three primary frequency bands: Low Frequency (LF), . RFID operates across three primary frequency bands: Low Frequency (LF), High Frequency (HF), and Ultra-High Frequency (UHF). In this guide, we’ll explore the characteristics of each band, their applications, and how to choose the one that best fits your needs.
When choosing an RFID tag, one important but not-often-thought-of decision to make is the frequency of the tag, such as LF, HF or UHF. Which do you choose? low frequency (LF, 30 KHz to 300 kHz; typically LF systems work at 125 KHz)
Typically, passive RFID systems use either low frequency (LF), high frequency (HF), or ultra-high frequency (UHF). Based on a schematic overview, this blog article provides an initial guide to these frequency ranges and their characteristics.This article will analyze in detail the characteristics and application differences of the three RFID frequencies: LF (low frequency), HF (high frequency), and UHF (ultra-high frequency). Low Frequency RFID & High Frequency RFID have 8 key differences that set them apart - the actual frequency range , data rates, write capabilities, environmental concerns, read range, tag formats, RFID applications, RFID hardware.
The three primary frequencies used with RFID devices include Low Frequency (LF), High Frequency (HF), and Ultra High Frequency (UHF). But what’s the difference between these frequencies? Well, each of the three frequencies behaves differently when .
What are RFID tags? Comparing ultra-high-frequency (UHF) vs. high-frequency (HF) vs. near field communication (NFC) vs. low-frequency (LF) RFID tag types. An explanation of the difference between active, passive and semi-passive RFID tags.
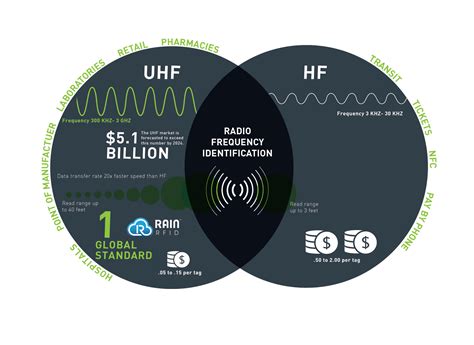
RFID tags operate at different frequencies: LF (Low Frequency) 125-134.2 kHz, HF (High Frequency) 13.56 MHz, and UHF (Ultra-High Frequency) 860-960 MHz. LF tags, with a short read range, are commonly used for access control and inventory management in retail and healthcare industries.Ultra-High-Frequency RFID (UHF) Ultra-high-frequency RFID operates at frequencies between 300 MHz and 3 GHz. This range provides even longer reading distances, typically up to 12 meters or more. UHF RFID is widely used in supply chain management, asset tracking, and retail inventory management.
The ultra-high frequency band is able to cover frequencies from 300 MHz to 3 GHz (Gigahertz). The read range of the UHF is up to 12 meters, which is 40 feet. As a result, ultra-high frequency systems operate around 900 to 915 MHz. The UHF RFID . RFID operates across three primary frequency bands: Low Frequency (LF), High Frequency (HF), and Ultra-High Frequency (UHF). In this guide, we’ll explore the characteristics of each band, their applications, and how to choose the one that best fits your needs. When choosing an RFID tag, one important but not-often-thought-of decision to make is the frequency of the tag, such as LF, HF or UHF. Which do you choose? low frequency (LF, 30 KHz to 300 kHz; typically LF systems work at 125 KHz) Typically, passive RFID systems use either low frequency (LF), high frequency (HF), or ultra-high frequency (UHF). Based on a schematic overview, this blog article provides an initial guide to these frequency ranges and their characteristics.
rfid vs hf
This article will analyze in detail the characteristics and application differences of the three RFID frequencies: LF (low frequency), HF (high frequency), and UHF (ultra-high frequency).
rfid range
Low Frequency RFID & High Frequency RFID have 8 key differences that set them apart - the actual frequency range , data rates, write capabilities, environmental concerns, read range, tag formats, RFID applications, RFID hardware. The three primary frequencies used with RFID devices include Low Frequency (LF), High Frequency (HF), and Ultra High Frequency (UHF). But what’s the difference between these frequencies? Well, each of the three frequencies behaves differently when . What are RFID tags? Comparing ultra-high-frequency (UHF) vs. high-frequency (HF) vs. near field communication (NFC) vs. low-frequency (LF) RFID tag types. An explanation of the difference between active, passive and semi-passive RFID tags. RFID tags operate at different frequencies: LF (Low Frequency) 125-134.2 kHz, HF (High Frequency) 13.56 MHz, and UHF (Ultra-High Frequency) 860-960 MHz. LF tags, with a short read range, are commonly used for access control and inventory management in retail and healthcare industries.
Ultra-High-Frequency RFID (UHF) Ultra-high-frequency RFID operates at frequencies between 300 MHz and 3 GHz. This range provides even longer reading distances, typically up to 12 meters or more. UHF RFID is widely used in supply chain management, asset tracking, and retail inventory management.
lenovo t410 smart card reader driver
la tua nuova smart card sky
rfid frequency
NTAG215 chips are a type of Near-Field Communication chip. They’re only known for being used in amiibo figures and cards, and they’re very cheap. You can order them in bulk from Chinese companies for hardly .
lf hf uhf rfid|high frequency rfid