advantages of rfid tag reader Tag Activation: The RFID reader emits radio frequency signals via its antenna. A passive RFID tag receives the signal and uses that energy to power up its microchip, while an active tag . The problems seems to be that it's not possible to emulate/modify the sector 0, which is often the UID (identifier). This question is linked (but probably outdated). It is possible .
0 · what is rfid technology
1 · rfid advantage and disadvantages
2 · radio frequency rfid advantages
3 · pros and cons of rfid
4 · disadvantages of rfid technology
5 · advantages of rfid tags
6 · advantages of rfid scanner
7 · advantages of rfid
It’s all too easy to steal not just your credit card—but all the information tied to it. Loyola's own cybersecurity expert Assistant Professor of Computer Science Eric Chan-Tin, says nearly every individual who possesses a credit card is already .
Tag Activation: The RFID reader emits radio frequency signals via its antenna. A passive RFID tag receives the signal and uses that energy to power up its microchip, while an active tag . Radio frequency identification or RFID is a wireless technology for automatically identifying and tracking tags or smart labels using electromagnetic fields. Some of its notable applications include contactless payment for toll gates, tracking and managing inventory, other contactless payment and point-of-sale solutions, asset tracking .
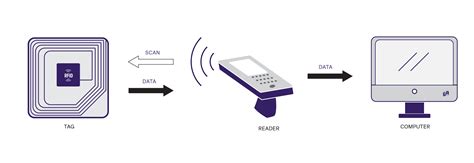
Tag Activation: The RFID reader emits radio frequency signals via its antenna. A passive RFID tag receives the signal and uses that energy to power up its microchip, while an active tag directly sends a response. Readers, also called interrogators, are devices that transmit and receive radio waves to communicate with RFID tags. In terms of mobility/flexibility, RFID readers are typically divided into three distinct types: Fixed RFID Readers, Mobile RFID Readers, and USB Readers. RFID tags contain an integrated circuit and an antenna, which are used to transmit data to the RFID reader (also called an interrogator). The reader then converts the radio waves to a more usable form of data. The fundamentals of an RFID system lie in the relationship between two core components: the RFID tag and the RFID reader. The tag contains an integrated circuit for storing and processing information, along with an antenna to receive and transmit the signal.
Antenna. RFID tags transmit data to the RFID reader, converting the radio waves to a more unstable form of data. Thus, the tags information collected is used to transfer to the host computer system, where the data is stored in a database and analysed later.
Portability and flexibility. RFID handheld tag reader with its lightweight design, is easy to adapt to a variety of complex work environments. Whether on small warehouse shelves, or in a busy retail store, can be flexible to cope with, and quickly complete the task. Barcode labels can be very inexpensive (a matter of a few cents per label) whereas RFID tags can run the gamut from /tag to upwards of /tag, all dependent upon the type of tags you need. RFID readers are also a bit pricier than barcode scanners.
While RFID offers many advantages, challenges include initial setup complexity, higher costs compared to traditional tracking methods, potential signal interference, and the need for ongoing maintenance, especially for active tags with batteries. Asset tracking software like RedBeam is essential for the effective use of RFID technology.
But how exactly does this technology work? RFID Tags: An Overview. An RFID tag is a tiny computer chip attached to an antenna in a compact form, transmitting information to an RFID reader through radio waves. There are several types of RFID tags, each operating at a different frequency.
Radio frequency identification or RFID is a wireless technology for automatically identifying and tracking tags or smart labels using electromagnetic fields. Some of its notable applications include contactless payment for toll gates, tracking and managing inventory, other contactless payment and point-of-sale solutions, asset tracking .Tag Activation: The RFID reader emits radio frequency signals via its antenna. A passive RFID tag receives the signal and uses that energy to power up its microchip, while an active tag directly sends a response.
Readers, also called interrogators, are devices that transmit and receive radio waves to communicate with RFID tags. In terms of mobility/flexibility, RFID readers are typically divided into three distinct types: Fixed RFID Readers, Mobile RFID Readers, and USB Readers. RFID tags contain an integrated circuit and an antenna, which are used to transmit data to the RFID reader (also called an interrogator). The reader then converts the radio waves to a more usable form of data.
The fundamentals of an RFID system lie in the relationship between two core components: the RFID tag and the RFID reader. The tag contains an integrated circuit for storing and processing information, along with an antenna to receive and transmit the signal. Antenna. RFID tags transmit data to the RFID reader, converting the radio waves to a more unstable form of data. Thus, the tags information collected is used to transfer to the host computer system, where the data is stored in a database and analysed later.
Portability and flexibility. RFID handheld tag reader with its lightweight design, is easy to adapt to a variety of complex work environments. Whether on small warehouse shelves, or in a busy retail store, can be flexible to cope with, and quickly complete the task. Barcode labels can be very inexpensive (a matter of a few cents per label) whereas RFID tags can run the gamut from /tag to upwards of /tag, all dependent upon the type of tags you need. RFID readers are also a bit pricier than barcode scanners. While RFID offers many advantages, challenges include initial setup complexity, higher costs compared to traditional tracking methods, potential signal interference, and the need for ongoing maintenance, especially for active tags with batteries. Asset tracking software like RedBeam is essential for the effective use of RFID technology.
what is rfid technology
rfid advantage and disadvantages
Card or Passport or Driving License alongwith an undertaking. No paper Admit Card will be .
advantages of rfid tag reader|what is rfid technology