passive rfid tag memory Passive RFID Tags. Passive RFID tags contain a low-power integrated circuit (IC) attached to . Over 70,000 EasyCard transactions happen daily in Taiwan. 11 million EasyCards are used daily across Taiwan. Stored funds on EasyCard have increased 97% from 2022. Users can load up to NT$10,000 on a single card. .
0 · smallest passive rfid tag
1 · rfid tags passive vs active
2 · rfid passive tag cost
3 · range of passive rfid tags
4 · passive rfid tags for sale
5 · passive rfid tag price
6 · passive rfid tag example
7 · long range passive rfid tags
Here's an updated look at the NFC West wild-card playoff picture. Minnesota Vikings remain in No. 1 wild card spot. . the guys recap last weekend’s Premier League results. .

Passive RFID systems are composed of three components – an interrogator (reader), a passive tag, and a host computer. The tag is composed of an antenna coil and a silicon chip that includes basic modulation circuitry and non-volatile memory.Passive RFID Tags. Passive RFID tags contain a low-power integrated circuit (IC) attached to .Passive RFID systems are composed of three components – an interrogator (reader), a passive tag, and a host computer. The tag is composed of an antenna coil and a silicon chip that includes basic modulation circuitry and non-volatile memory.
Passive RFID Tags. Passive RFID tags contain a low-power integrated circuit (IC) attached to an antenna, and are enclosed with pro-tective packaging (like a plastic card) as determined by the application. On-board memory within the IC stores data.Passive RFID tags harness energy from an RFID reader’s emitted Radio-frequency (RF) signal. When the reader sends a signal, it creates an electromagnetic field that energizes the tag. The tag captures this energy and powers its internal chip, enabling it to transmit data back to the reader. In a passive RFID system, RFID tags don’t contain batteries and tags use the radio wave signals coming from the reader to transmit the encoded data as RF signals. The tag antenna captures the signal and powers up the microchip inside the tag. Passive RFID tags typically store anywhere from 64 bits to 1 kilobyte of non-volatile memory. Originally, tags contained sufficient memory to store only a unique serial number or “license plate,” and perhaps some additional information.
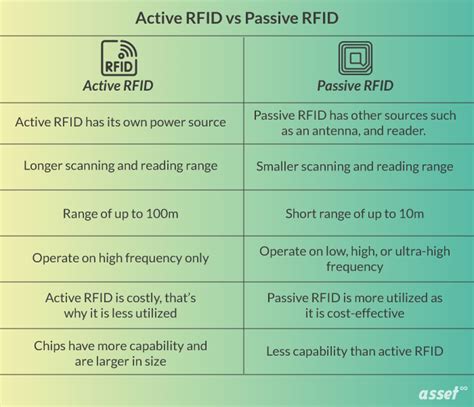
Passive tags are widely favored for their affordability and versatility in diverse operational environments. Understanding the fundamental differences and advantages of active and passive RFID tags is crucial for implementing an effective RFID strategy tailored to specific business needs.
smallest passive rfid tag
Discover the essentials of RFID passive tags, including their advantages, applications, and limitations. Learn how modern technology addresses these challenges and helps you make informed decisions for your RFID needs. Passive RFID tags are lightweight, cost-effective, and have a longer lifespan compared to active RFID tags. They are available in various form factors, making them versatile in terms of integration into different objects and applications. RFID tags, the core components of RFID systems, come in two main types: passive and active tags. Passive RFID tags rely on external RF energy emitted by RFID readers to power their operation. These tags are cost-effective, . Passive RFID Tags. Passive RFID tags are an integral part of many tracking and identification systems. These tags rely on the energy emitted by RFID readers to power their operation. They are commonly used in applications where .
Passive RFID systems are composed of three components – an interrogator (reader), a passive tag, and a host computer. The tag is composed of an antenna coil and a silicon chip that includes basic modulation circuitry and non-volatile memory.
rfid tags passive vs active
Passive RFID Tags. Passive RFID tags contain a low-power integrated circuit (IC) attached to an antenna, and are enclosed with pro-tective packaging (like a plastic card) as determined by the application. On-board memory within the IC stores data.Passive RFID tags harness energy from an RFID reader’s emitted Radio-frequency (RF) signal. When the reader sends a signal, it creates an electromagnetic field that energizes the tag. The tag captures this energy and powers its internal chip, enabling it to transmit data back to the reader.
In a passive RFID system, RFID tags don’t contain batteries and tags use the radio wave signals coming from the reader to transmit the encoded data as RF signals. The tag antenna captures the signal and powers up the microchip inside the tag.
Passive RFID tags typically store anywhere from 64 bits to 1 kilobyte of non-volatile memory. Originally, tags contained sufficient memory to store only a unique serial number or “license plate,” and perhaps some additional information. Passive tags are widely favored for their affordability and versatility in diverse operational environments. Understanding the fundamental differences and advantages of active and passive RFID tags is crucial for implementing an effective RFID strategy tailored to specific business needs.
Discover the essentials of RFID passive tags, including their advantages, applications, and limitations. Learn how modern technology addresses these challenges and helps you make informed decisions for your RFID needs. Passive RFID tags are lightweight, cost-effective, and have a longer lifespan compared to active RFID tags. They are available in various form factors, making them versatile in terms of integration into different objects and applications. RFID tags, the core components of RFID systems, come in two main types: passive and active tags. Passive RFID tags rely on external RF energy emitted by RFID readers to power their operation. These tags are cost-effective, .
nfc sim card singapore
nfc debit card hdfc
rfid passive tag cost
$35.96
passive rfid tag memory|range of passive rfid tags